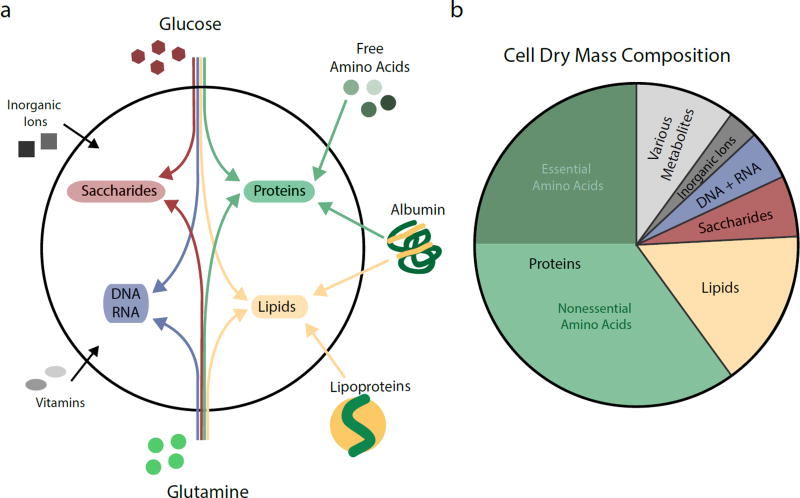
Figure 1. The Nutritional Requirements for Mammalian Cell Growth.
a, Contributions of major nutrients present in mammalian circulation towards the synthesis of cellular macromolecules. Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are synthesized intracellularly from glucose and glutamine. Other non-essential amino acids can also contribute to nucleotide production (not shown). Saccharides are derived from glucose, with nitrogen groups being donated by glutamine. Amino acids for protein synthesis can be imported in their free form or derived from catabolism of extracellular proteins. Non-essential amino acids can also be synthesized from glucose and glutamine. Extracellular lipids are delivered by lipoproteins and serum albumins. Most lipids are not essential for mammalian cells and can also be generated from glucose and glutamine carbons. Cells further require exogenous supply of a variety of essential micronutrients such as inorganic ions and vitamins. b, Fractional contribution of proteins, lipids, saccharides, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), inorganic ions and metabolites to dry mass of a representative mammalian cell. The proportion of essential and non-essential amino acids contained within proteins are indicated.