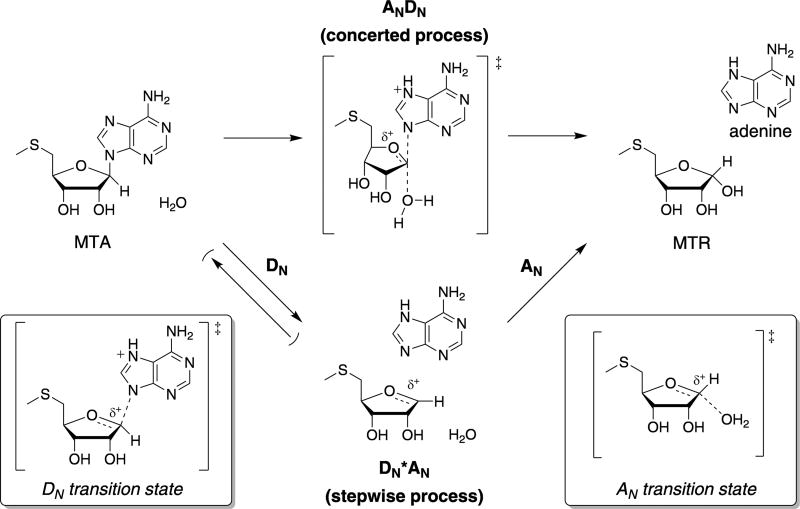
Figure 3.
General mechanisms for the hydrolysis of MTA by Rv0091. The Rv0091 reaction is represented as two possible mechanisms in which the transformations are considered as their elementary steps. For MTA hydrolysis, the AN step refers to the association of the water nucleophile and the DN step refers to dissociation of the adenine leaving group. If the reaction proceeds through a concerted bimolecular TS, the mechanism is termed ANDN. If dissociation of the leaving group precedes association of the nucleophile and the reaction proceeds through a stepwise process via discrete transition states, the reaction is termed DN*AN. For DN*AN processes, a superscript “‡” is used to denote the rate-limiting step, e.g., DN‡*AN or DN*AN‡. MTA, 5′-methylthioadenosine; MTR, 5′-methylthioribose.