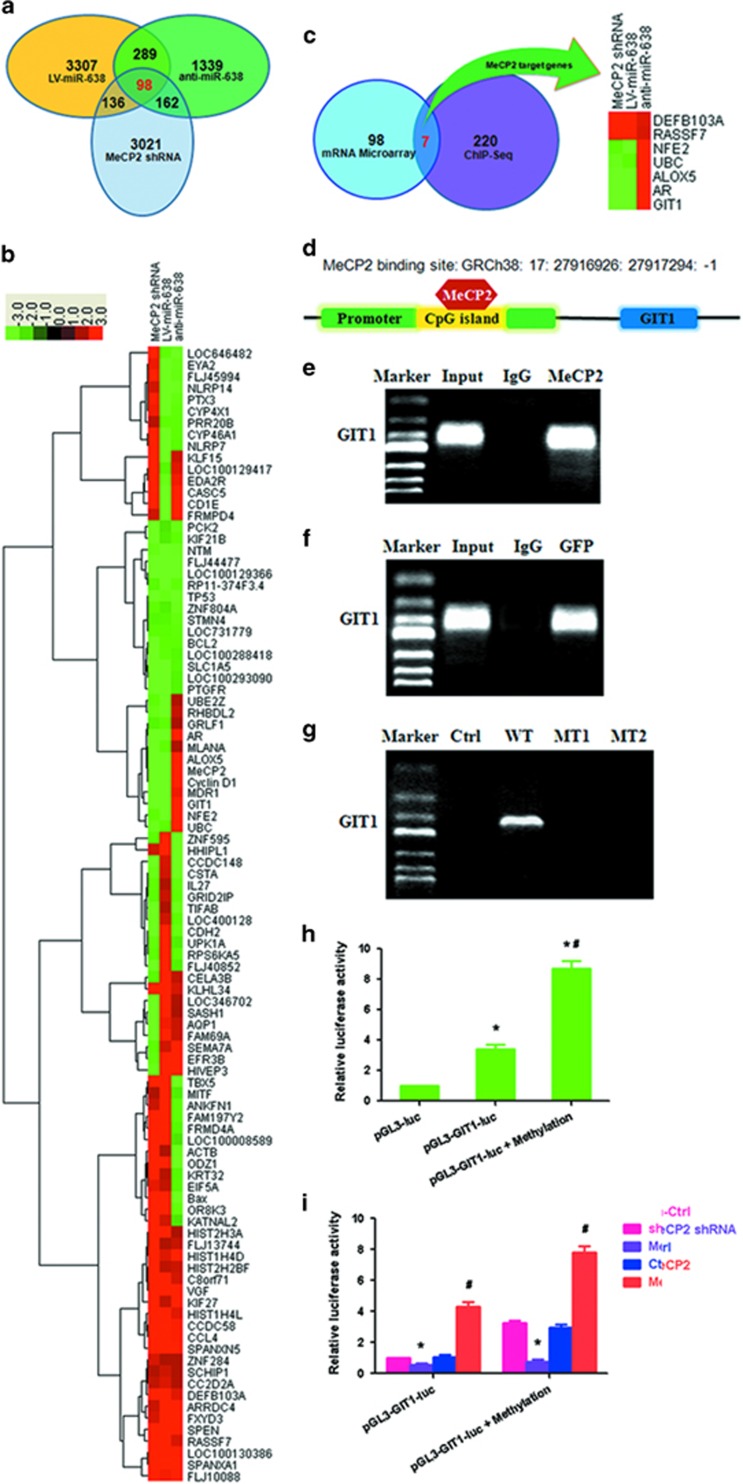
Figure 5.
MeCP2 binds to the promoter regions of GIT1 in GC cells. (a) Overlapping genes (n=98) after transfection with MeCP2 shRNA, LV-miR-638 or anti-miR-638. (b) Heat map of 98 overlapping genes with fold change⩾2.0 after transfection with MeCP2 shRNA, LV-miR-638 or anti-miR-638. (c) Overlapping genes (n=98) after transfection with MeCP2 shRNA, LV-miR-638 or anti-miR-638 compared with 220 genes corresponding to ChIP-Seq peaks located in the promoter. (d) MeCP2 binding site in the promoter of GIT1. (e) ChIP–RT–PCR of GIT1 performed with anti-MeCP2 antibody. (f) ChIP–RT–PCR of GIT1 performed with anti-GFP antibody after transfection with GFP-MeCP2 plasmid. (g) ChIP–RT–PCR of GIT1 performed with anti-GFP antibody after transfection with Ctrl (GFP), WT (GFP-MeCP2), MT1 (GFP-Mutation type 1) or MT2 (GFP-Mutation type 2) plasmids. (h) BGC-823 cells were transfected with pGL3-GIT1-luc (target sequences of promoter regions of GIT1) or pGL3-GIT1-luc+methylation; luciferase activity was determined at 48 h post-transfection. Renilla luciferase served as the internal control. *P<0.01 compared with pGL3-luc. #P<0.01 compared with pGL3-GIT1-luc. (i) BGC-823 cells were treated with pGL3-GIT1-luc, methylation, MeCP2 shRNA or MeCP2 overexpression vector; luciferase activity was determined. *P<0.01 compared with sh-Ctrl. #P<0.01 compared with Ctrl.