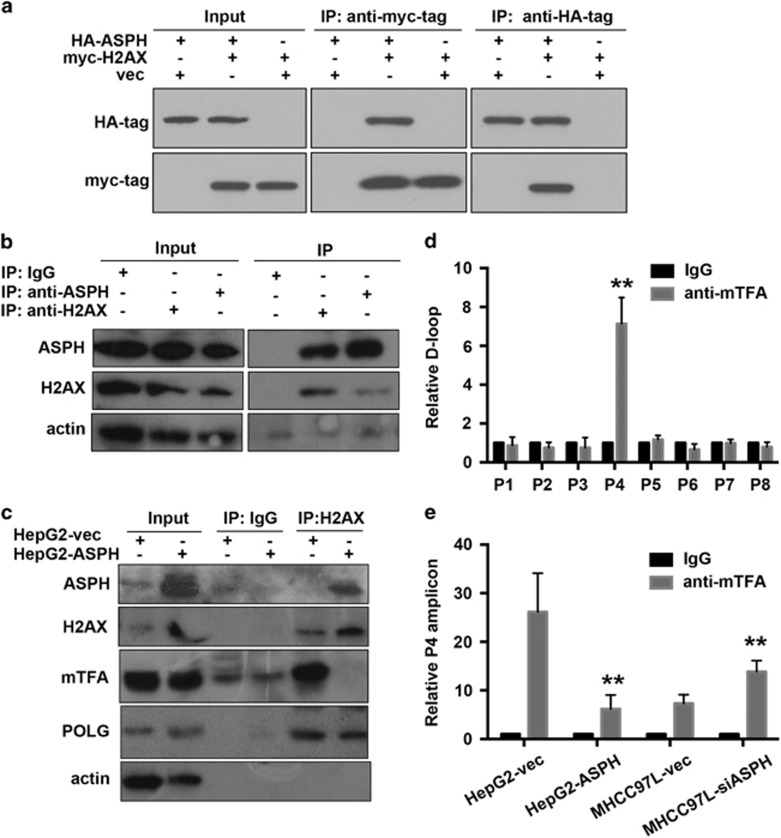
Figure 6.
ASPH competes with mtTFA in interacting with H2AX in HCC cell lines. (a) Interaction between exogenously expressed HA-tagged ASPH and myc-tagged H2AX in 293 cells assayed by immunoprecipitation using HA antibody or myc antibody. (b) Interaction of endogenous ASPH and H2AX in MHCC-97 L cells assayed by immunoprecipitation using ASPH antibody or H2AX antibody. (c) Influence of ASPH overexpression on mTFA–H2AX interaction. The protein complex that was immunoprecipitated by H2AX antibody in HepG2 cells overexpressed with ASPH and control vectors was further analyzed by immunoblot using ASPH, POLG and mTFA antibodies. (d) Identification of mTFA-binding mtDNA motif in the D-loop region through a chromosome immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-PCR assay. The protein–DNA complex was immunoprecipitated by mTFA antibody in MHCC-97 L cells. The putative bound mtDNA motif was further amplified using eight primer pairs that covered the D-loop region and were designated from P1 to P8. The amplicon of primer set 4 (P4) showed enrichment in the protein–DNA motif. **P<0.01 vs IgG group. (e) Influence of ASPH overexpression on mTFA-binding probability to D-loop region through a ChIP-PCR assay. The amounts of D-loop region characterized by P4 amplicon in the mTFA–DNA complex were analyzed in HepG2 cells overexpressed with ASPH or MHCC-97 L cells with silenced ASPH in comparison to the control group overexpressed with vectors. All data are shown as mean±s.d. from at least three independent experiments. **P<0.01 vs vector group.