Figure 2. Facial motor pools exhibit a loose spatial topography that is maintained in caudal migration mutants.
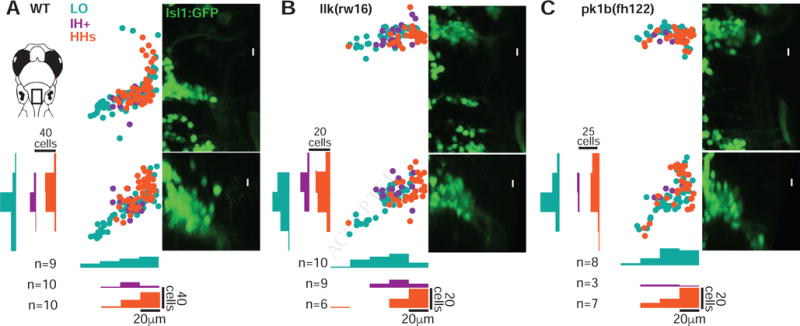
(A) Across wild type larvae, the LO motor pool (teal) extends throughout the entire facial motor nucleus, while the IH+ (purple) and HHs (orange) motor pools are found in more restricted but still overlapping regions – in the middle and dorsomedial portions of the nucleus, respectively. In llk(rw16) mutant larvae (B) and pk1b(fh122) mutant larvae (C), the cross-sectional topography of the motor pools is maintained (Table S1). All fish were backfilled at 4dpf and imaged at 5dpf. n = number of fish used in each condition. Histograms illustrate the distribution of cells along the mediolateral and dorsoventral axes, binned at 20μm intervals. LO = levator operculi, IH+ = interhyoideus + hyohyoideus inferior, HHs = hyohyoideus superior. See also Figure S1.
