Figure 3. Facial motor neurons are topographically organized according to age in both wild type and caudal migration mutants.
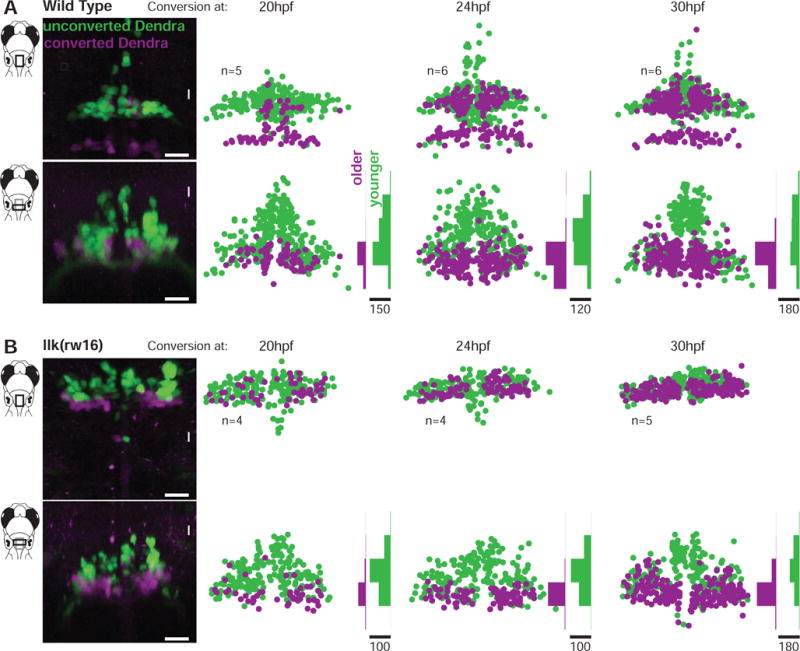
Zebrafish embryos expressed the photo convertible protein Dendra2 in cranial motor neurons and were exposed to ultraviolet light at one of three time points during facial motor neuron differentiation (20, 24 or 30 hpf), then imaged at 3dpf. Neurons older than the conversion time point contain converted (magenta/purple) Dendra, while younger neurons contain only unconverted (green) Dendra. In both wild type (A) and llk(rw16) mutant (B) larvae, older facial motor neurons are located in the ventral-most part of the facial motor nucleus. Examples in left panels of (A) and (B) have been color adjusted to increase visibility of the converted (magenta) Dendra signal. n = number of fish used in each condition. Histograms illustrate the distribution of cells along the dorsoventral axis binned at 20μm intervals, where the scale bars refer to the number of cells. See Figure S2 for data from pk1b(fh122) mutants.
