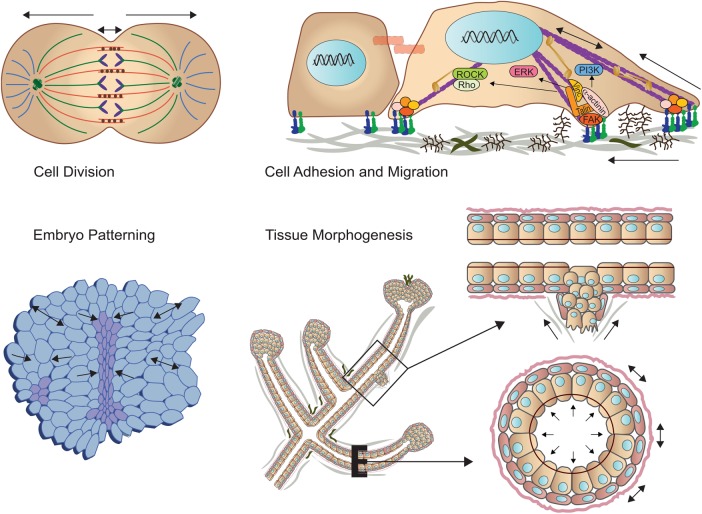
FIGURE 1:
Mechanical force across length scales regulates cell behavior and tissue development. (Top left) Spindle forces are critical for cell division. (Top right) The stiffness of the extracellular matrix promotes focal adhesion assembly to modulate cell migration. (Bottom left) Cell–cell force dictates embryonic patterning. (Bottom right) Tissue-level forces modulate branching morphogenesis and when corrupted can foster cell invasion.