Figure 6.
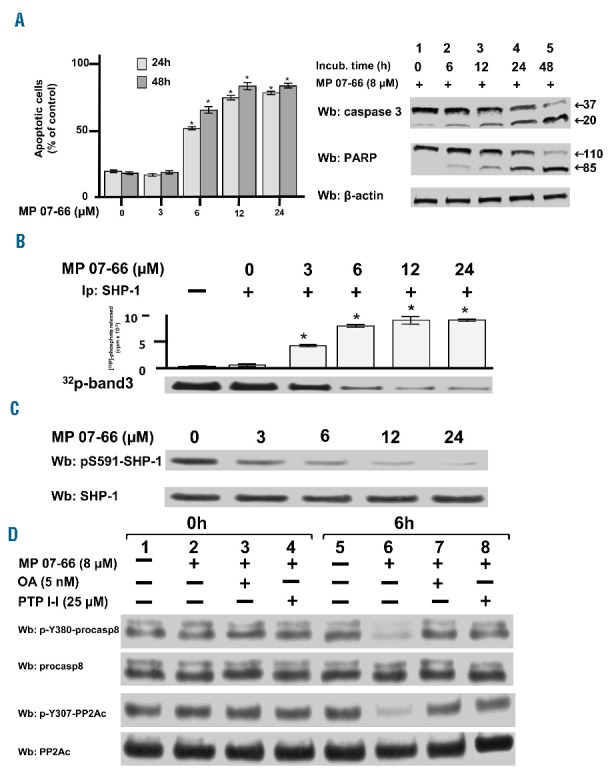
Effect of MP 07-66 on the chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell survival. (A) Apoptosis of CLL cells from ten patients belonging to the various clinical and biological subtypes cultured in the presence of increasing concentrations of MP07-66 for 24 and 48 h analyzed by annexin V– propidium iodide flow cytometry (left-hand panel). Data are mean percentages of early and late apoptosis ± SD from three separate experiments performed in triplicate (*P≤0.01). Western blotting (Wb) analysis of total cell lysate of CLL cells with anti-caspase 3 and anti-PARP antibodies monitored caspase-dependent apoptosis; anti-β-actin antibody was used as a loading control (right-hand panel). (B) Tyrosine phosphatase activity of SHP-1 immunoprecipitated from the cytosol of CLL cells of patient #28 cultured in the presence of increasing concentrations of MP07-66 for 1 h and measured as [32P] released from in vitro [32P]-Band 3. Data are expressed as mean ± SD from one experiment performed in triplicate (*P≤ 0.01). (C) Expression of SHP-1 and phosphorylation state of pS591 of CLL cells of patient #28 cultured in the presence of increasing concentrations of MP07-66. Data are expressed as mean ± SD from one experiment performed in triplicate (*P≤0.01). (D) Expression and phosphorylation state of procasp8 and PP2Ac in the CLL cells of patient #28 cultured in the absence (lanes 1 and 5) and presence of 8 μM MP07-66 supplemented with 5 nM okadaic acid (OA) (lanes 3 and 7) or 25 μM PTP-I-I (lanes 4 and 8) for 0 and 6 h.
