Figure 1.
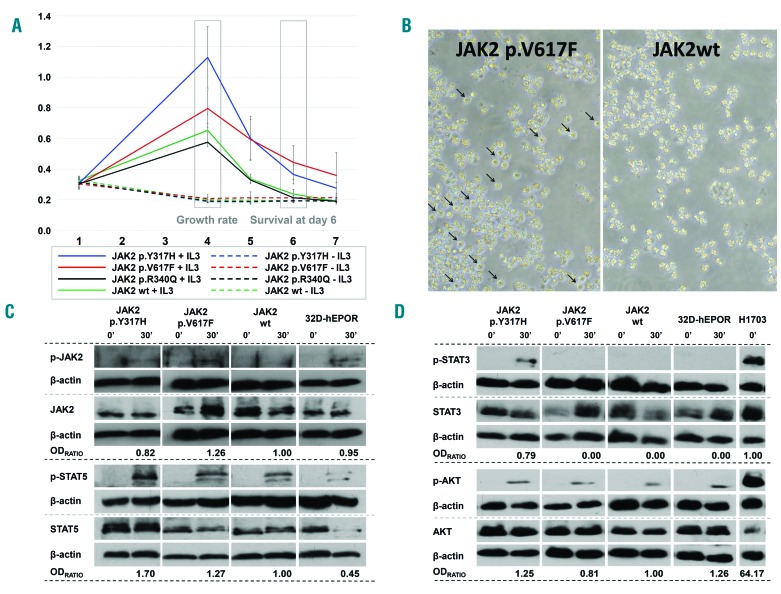
Results from 32D-hEPOR cells expressing p.V617F and p.Y317H JAK2 mutations. (A) MTS assays. Graph shows the relative proliferation of p.V617F, p.Y317H and p.R340Q mutants compared to wild-type JAK2 expressing cells in two different conditions (with or without WEHI medium as a source of murine IL-3). The relative absorbance at 492 nm (Y-axis) which is directly proportional to the number of cells, was quantified daily for 7 days (X-axis). The growth rate was calculated as the difference between the maximum absorbance achieved and the absorbance at day 1. Day 6 cell survival was calculated as the difference between the absorbance at day 6 and 1. None of the mutations were able to promote cytokine-independent growth (including p.V617F JAK2 mutation). The p.V617F mutation caused hypersensitivity to IL-3 (P = 0.043) and a significantly higher survival at day 6 (P < 0.05). Cells with p.Y317H showed a higher growth rate and an enhanced cell survival at day 6 compared to wild-type JAK2 cells (P < 0.001) and a higher growth rate compared to p.V617F cells (P < 0.001). Cells with the p.R340Q mutation did not show differences with wild-type JAK2 cells (P = 0.427). (B) Viability of cells (32D-hEPOR-V617FJAK2 vs. 32D-hEPOR-wtJAK2) cultured without IL-3 at day 6. Survival of cells expressing p.V617F mutants (live cells marked with arrows) could be observed under optic microscope; by contrast, cells expressing wild-type JAK2 underwent a rapid cell death. (C,D) Western blot analyses showing JAK2, STAT5, STAT3 and AKT phosphorylation before and after stimulation with IL-3 and hEPO. Cells were starved for 6 h and then stimulated for 30 min with hEPO (5 U/mL) and 20% of undiluted IL-3 conditioned WEHI-3B medium. Intensities of specific bands corresponding to the proteins of interest were measured by relative densitometry (optic density (OD) × mm) to β-actin. The activation of each protein was obtained dividing the relative OD of the phosphorylated protein by the relative OD of the non-phosphorylated form. OD ratio shows the level of activation of the mutated form divided by the level of activation of the wild type. In the case of STAT3, this ratio was obtained dividing the level of activation of the mutated form by the level of activation in the positive control (H1703) because STAT3 activation was not detected in JAK2 wild-type. Results show that p.Y317H mutation was less active than p.V617F on JAK2 phosphorylation, but it has a greater effect on STAT5 phosphorylation (~1.70 vs. ~1.27-fold higher) as well as on AKT phosphorylation (~1.25 vs. ~0.81-fold higher) upon cytokine stimulation. It also promoted STAT3 phosphorylation, whereas p.V617F did not. hEPOR: human erythropoietin receptor; 32D-hEPOR-V617FJAK2: 32D cells stably expressing hEPOR and p.V617F; 32D-hEPOR-wtJAK2: 32D cell stably expressing hEPOR and wild-type JAK2; IL-3: interleukin 3; hEPO: human erythropoietin; OD: optic density.