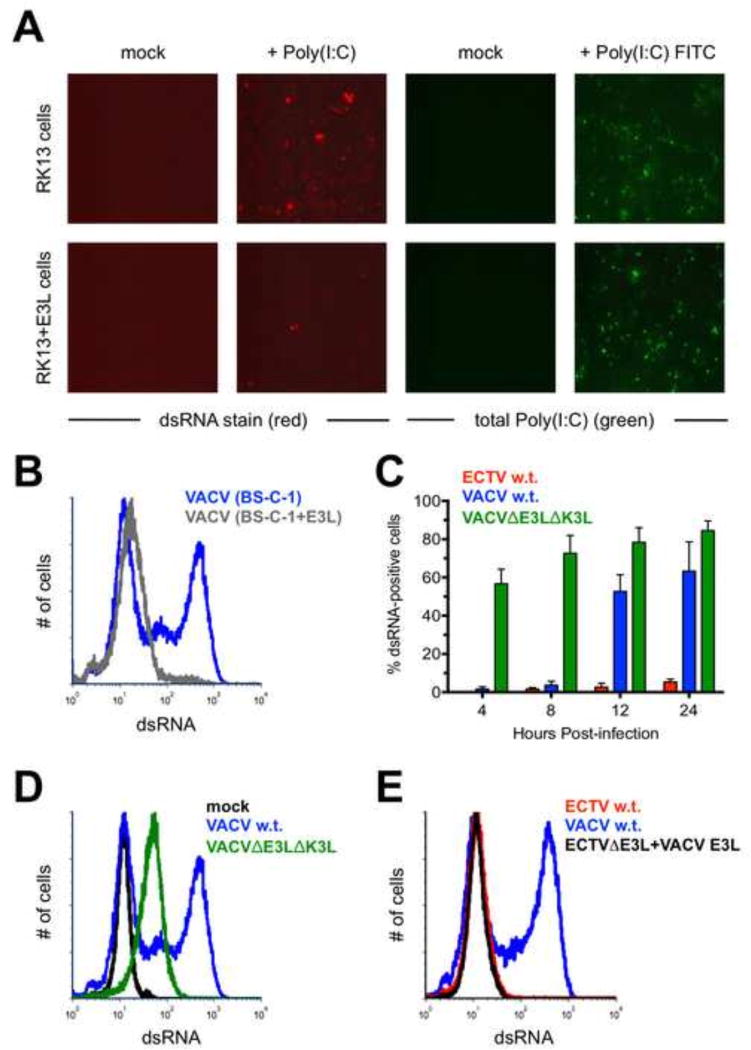
Figure 5. The E3 protein may prevent recognition of dsRNA by the J2 antibody.
(A) RK13 and RK13+E3L cells were transfected with 1 µg of Poly(I:C) or Poly(I:C) conjugated to fluorescein. The cells were stained for dsRNA (red) approximately 16 hrs. later. Images are at 400× total magnification and representative of two independent trials. (B) BS-C-1 or BS-C-1+E3L cells were infected (MOI=10) with either ECTV or VACV for 24 hrs. prior to staining for dsRNA. The flow cytometric data are depicted in histogram format and representative of three independent trials. (C) BS-C-1 cells were infected (MOI=10) with ECTV, wild-type VACV, or VACVΔE3LΔK3L for various lengths of time prior to staining for dsRNA using flow cytometry. The bars depict the average values and the error bars represent the standard deviations of three independent trials for each time point. (D) Representative flow cytometric data in histogram format are shown for BS-C-1 cells infected (MOI=10) with the indicated viruses. The cells were stained for dsRNA after 24 hrs. (E) BS-C-1 cells were infected (MOI=10) with VACV, wildtype ECTV, or a mutant ECTV in which the native E3L was replaced with the E3L gene from VACV. The cells were stained for dsRNA after 24 hrs. The flow cytometric data are depicted in histogram format and representative of two independent trials.