Figure 5. Inhibition of NFκB nuclear translocation blocks upregulation of P-gp in human iPS brain endothelial cells co-cultured with iPS-SOD1-A4V astrocytes.
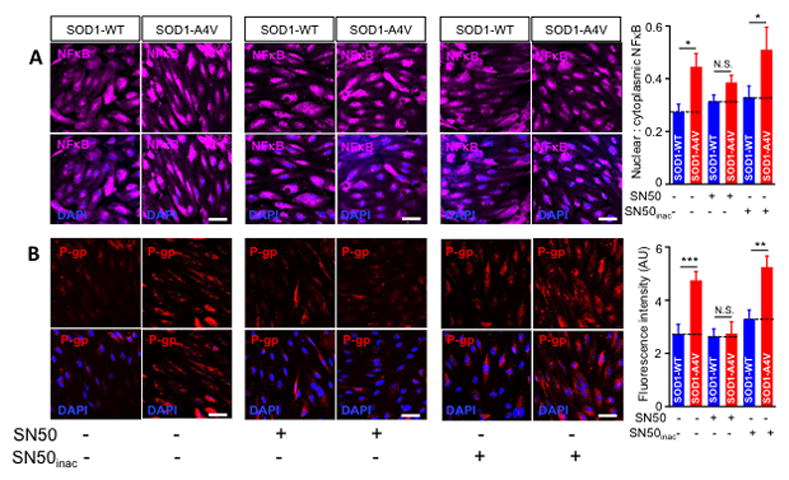
(A) Preincubation with SN50 1 μM effectively decreased the nuclear to cytoplasmic ratio of NFκB in human iPS brain endothelial cells co-cultured with iPS-SOD1-A4V astrocytes, whereas the inactive SN50 peptide was ineffective. Data are mean ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments (N.S. = not significant; * p < 0.05). 6–9 image fields were analyzed/group. (B) P-gp upregulation in endothelial cells co-cultured with SOD1-A4V astrocytes correlates with NFκB activity. Preincubation of endothelial cells with SN50 (1 μM) abolished the increase in P-gp, bringing it down to control levels. As expected, inactivated SN50 failed to reverse P-gp upregulation in endothelial cells co-cultured with hSOD1-A4V astrocytes. (Scale bar = 50 μm). 6–9 image fields were analyzed/group. Data are mean ± s.e.m. of three independent experiments (* p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, (*** p < 0.001).
