Figure 1. Structure, RNAP-inhibitory activity, and antibacterial activity of PUM.
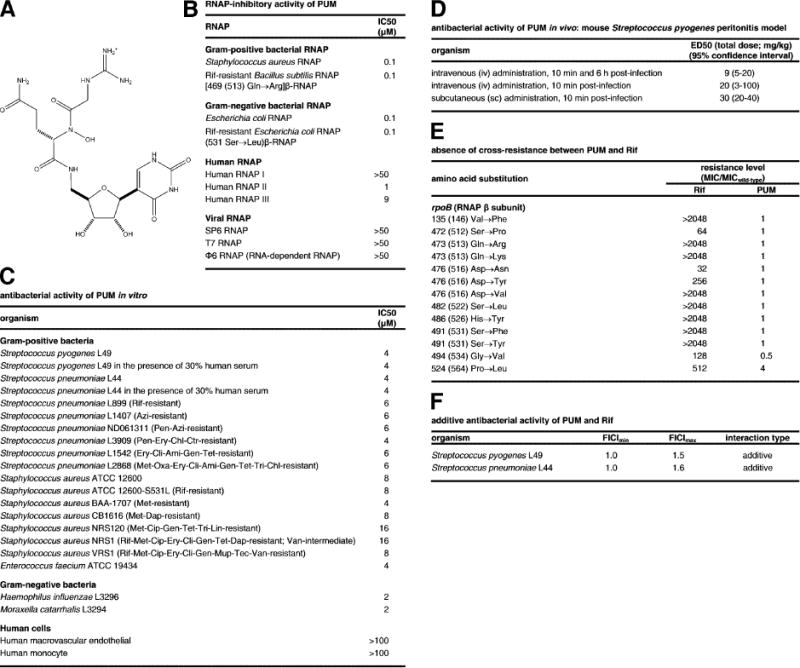
(A) Structure of PUM. (B) RNAP-inhibitory activity of PUM. (C) Antibacterial activity of PUM in vitro. (D), Antibacterial activity of PUM in vivo. Drug resistances are as follows: Ami. amikacin; Azi, azithromycin; Cip, ciprofloxacin; Ctr, ceftriaxone; Dap, daptomycin; Ery, erythromycin; Chl, chloramphenicol; Cli, clindamycin; Gen, gentamycin; Lin, linezolid; Met, methicillin; Mup, mupirocin; Pen, penicillin; Ox, oxacillin; Rif, rifampin; Tec, teicoplanin; Tet, tetracycline; Tri, trimethoprim; Van, vancomycin. (E) Absence of cross-resistance between PUM and Rif (data for S. pyogenes Rif-resistant mutants; residues numbered as in S. pyogenes and, in parentheses, E. coli). (F) Additive antibacterial activity of PUM and Rif.
