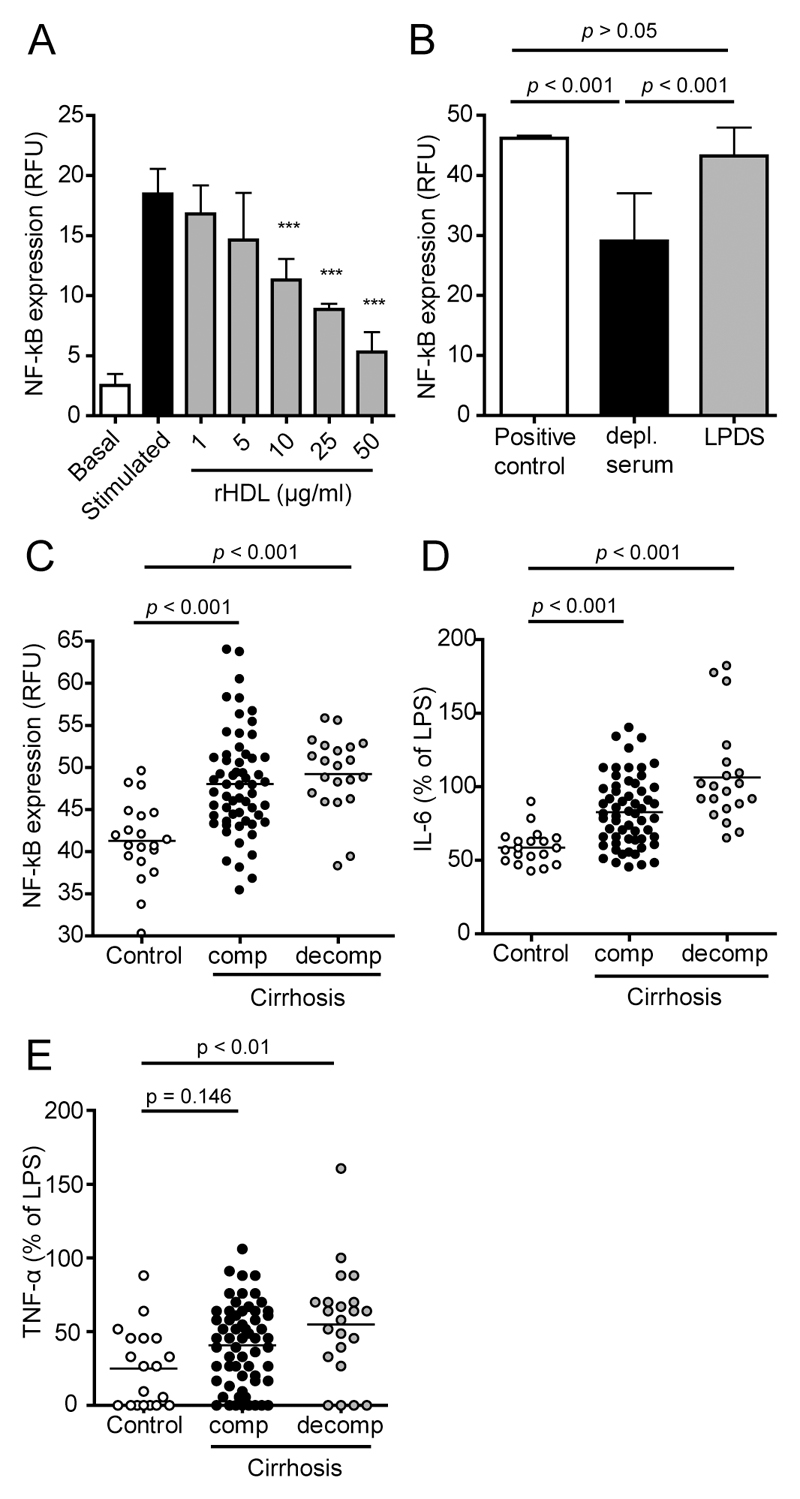
Figure 2. Cirrhosis is associated with reduced anti-inflammatory capacity of serum and a reduced ability to suppress the production of inflammatory cytokines.
Apolipoprotein B (apoB)-depleted sera of healthy subjects (control, n = 20), of patients with compensated (comp., n = 59) cirrhosis and of cirrhotic patients with acute decompensation (decomp., n = 21) were analyzed for their ability to inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation in monocytes. U937 monocytes containing a reporter cassette for NF-κB, were pretreated with (A) increasing concentrations (1-50 µg/mL) of reconstituted HDL (rHDL), (B) 10% lipoprotein deficient sera (LPDS) or (B,C) 7% apoB-depleted sera. After 1 ½ hours cells were stimulated with LPS (50 ng/mL) for 24 hours, followed by assessment of GFP expression by flow cytometry. (D,E) The supernatants of LPS stimulated monocytes which were pretreated with 7% apoB-depleted sera of patients or controls were analyzed for (D) interleukin-6 (IL-6) and (E) tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) concentrations using flow cytometry. All values shown represent means of two independent experiments measured in duplicates. RFU, relative fluorescence units.