Figure 3. Differential cytosine methylation influences CTCF binding.
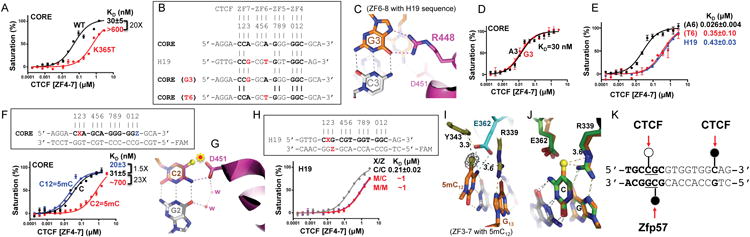
(A) A cancer-associated mutation (K365T) shows diminished DNA binding.
(B) The H19 sequence deviates from the CORE consensus sequence at two locations, a Gua instead of Ade at position 3 and a Thy instead of Ade at position 6.
(C) R448 of ZF7 makes bidentate contacts with the Gua at position 3 in the structure of ZF6-8 in complex with the H19 sequence.
(D) The Ade-to-Gua change at position 3 of the CORE sequence does not affect DNA binding affinity by ZF4-7.
(E) The Ade-to-Thy change at position 6 of the CORE sequence shows much reduced DNA binding by ZF4-7.
(F) Methylation at C2 of the CORE sequence abolishes DNA binding, whereas methylation of C12 enhances DNA binding by ZF4-7.
(G) Modeling a methyl group onto unmodified C2 potentially results in repulsion (indicated by a star) with D451 of ZF7.
(H) Methylation (hemi- or fully) of the CpG dinucleotide at position 2 of the H19 sequence shows reduced DNA binding affinity by ZF4-7.
(I) In the structure of ZF3-7 in complex with the methylated DNA, the omit electron density (grey mesh), contoured at 5σ above the mean, is shown for the 5mC methyl group (in yellow sphere).
(J) Structural comparison of ZF3-7 in complex with methylated DNA (in orange) and unmethylated DNA (in green).
(K) A model of strand-specific interaction associated with differential methylation at C2 by CTCF (open circle: un/de-methylated) and Zfp57 (filled circle: methylated). DNA binding data represent the mean ± SEM of two independent determinations performed in duplicate. See also Figure S3.
