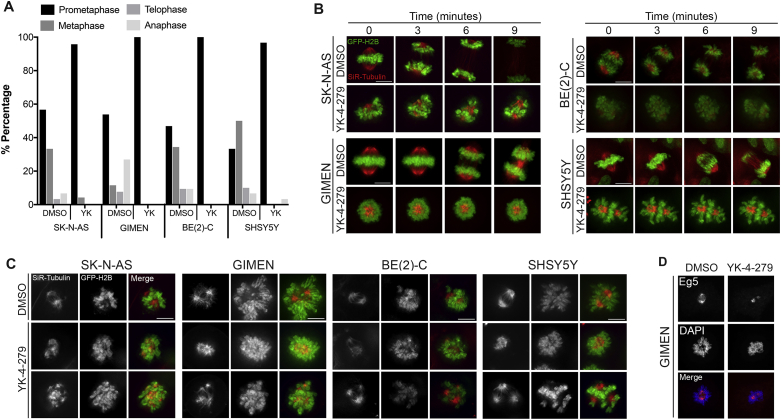
Fig. 4.
Disruption of mitosis induced by YK-4-279. (A) Four neuroblastoma cell lines, SK-N-AS, GIMEN, SK-N-BE(2)-C and SH-SY5Y were treated DMSO or with 1 μM YK-4-279 (5 μM was used for GIMEN). Prior to treatment cells were synchronized by standard double thymidine block protocol. Immediately after release, cells were treated with YK-4-279 for six hours. The graph shows the percentage of cells at distinct phases of mitosis, which were scored based on chromatin organization, in three independent replicates (n > 25). (B) SK-N-AS, GIMEN, SK-N-BE(2)-C and SH-SY5Y representative mitotic structures (Red: microtubules, Green: chromosomes) from three independent replicates. Diverse microtubule organization is evident from the images. All DMSO treated cells showed typical metaphase equatorial plates and progressed through mitosis and segregated chromosomes within the nine-minute time frame, whereas YK-4-279 cells were mostly stuck at prometaphase. (C) Static images of four live neuroblastoma cell lines. The range of abnormalities include fragmented (SK-N-AS), unseparated (GIMEN) and multipolar spindles (SK-N-BE(2)-C and SH-SY5Y) (Red: microtubules, Green: chromosomes). Images shown were representative of three independent replicates (n > 25). See also videos in Supplementary information. (D) Confocal microscopy showing immunofluorescent localization of Eg5 (pink) in YK-4-279-treated GIMEN cells. Chromatin is stained with DAPI (blue).