Figure 4. Effects of TKI treatment on monoclonal antibody-induced internalization and degradation.
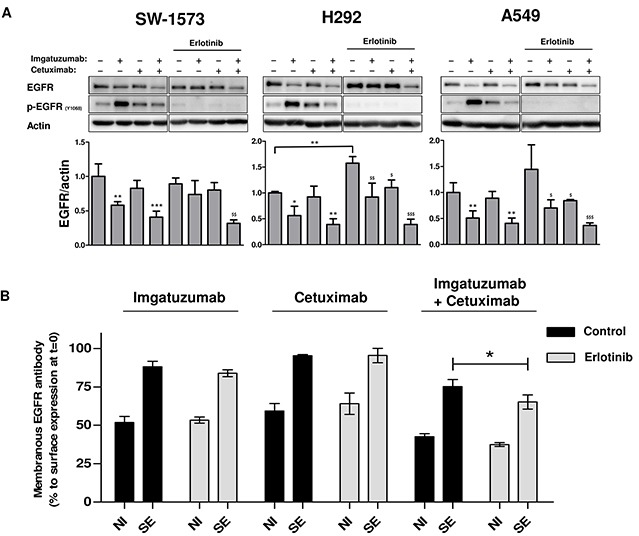
(A) Western blot analysis of the effect of 24 hours anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody treatment (20 μg/mL total) with or without erlotinib (10 μM) on EGFR total protein levels in SW-1573, H292 and A549. Data points are mean + SD. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared to untreated control; $P < 0.05, $$P < 0.01, $$$P < 0.001 compared to erlotinib treated control). (B) SW-1573 cells were pretreated for 24 hours with the EGFR TKI inhibitor erlotinib (10 μM). Cells were subsequently surface labeled with the anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies (20 μg/mL total) on ice and incubated at 37°C for 4 hours, and then analyzed for the non-internalized EGFR-antibody complexes (NI) and cell surface expression (SE). The lower the amount of non-internalized EGFR-antibody complexes, the higher the amount of internalized antibody-EGFR complexes. Surface expression of the control and erlotinib treated cells were both set at 100%. 24 hours erlotinib treatment resulted in a slight upregulation (10 – 15 % increase). Data points are mean ± SD (n = 3). (*P < 0.05).
