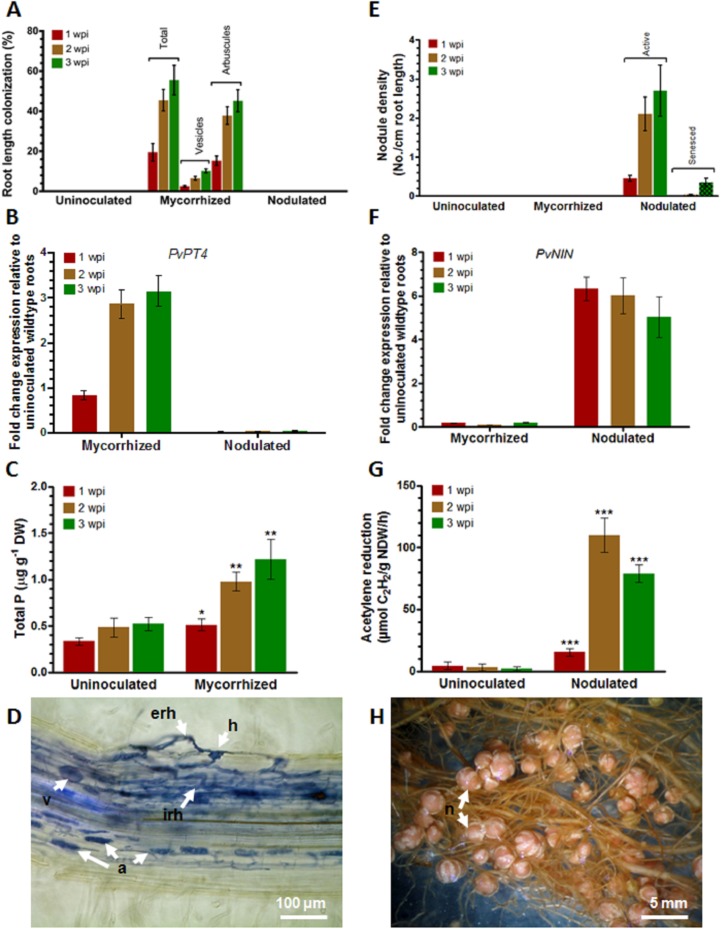
Fig 1. Determination of mycorrhizal and rhizobial colonization in P. vulgaris roots.
Control (uninoculated), mycorrhized (R. irregularis), and nodulated (R. tropici) root samples were assessed at different time points for symbiotic colonization. (A) Percent mycorrhizal root length colonization. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of mycorrhizal-induced PvPT4 transcript levels. (C) Total shoot phosphorus concentration. (D) Representative image showing fungal structures in trypan blue-stained roots at 2 weeks post inoculation (wpi) with R. irregularis. (E) Nodule density. (F) RT-qPCR analysis of rhizobial-induced PvNIN transcript levels. (G) Nitrogen-fixing activity measured by acetylene reduction assay. (H) Representative image showing root nodules at 2 wpi with R. tropici. erh, extraradical hyphae; h, hyphopodia; irh, intraradical hyphae, v, vesicle; a, arbuscule; n, nodule. Error bars on the graphs represent mean ± SD of three biological replicates (n = 9). Statistically significant differences are indicated by asterisks (unpaired two-tailed Student´s t test; *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001).