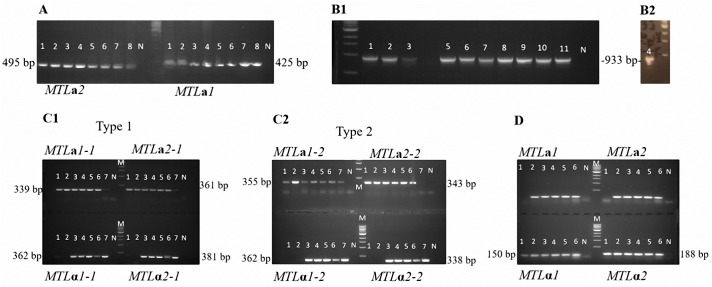
Fig 2.
Determination of the MTL genotypes by PCR, (a) Candida parapsilosis isolates (1–8 referring to CBS 8836, CBS 7248, CBS 2915, CBS 604, CBS 2216, CBS 8181, CBS 125.41, and CBS 1954), the 425 bp MTLa1 and the 495 bp MTLa2 products were obtained for all isolates; (b1 and b2) Lodderomyces elongisporus isolates (1–11 referring to the isolates 7660, 7661, 7663, 7665, 7666, 7668, 7669, 7670, 7672, 7673, and 7675), the 933 bp PCR product obtained for all isolates indicates the absence of any MTL transcription factor gene in between PIKa and orf19.3202; (c) Candida orthopsilosis isolates (1–7 referring to CBS 107.41, CBS 107.42, CBS 109.06, CBS 8825, CBS 107.43, CBS 9894, and CBS 2212) were screened with primers designed based on C. orthopsilosis type 1 (c1) and type 2 MTL sequences (c2); both primer pairs worked for the isolates although band brightness’ varied owing to differences among type 1 and type 2 sequences. With CBS 107.41 and CBS 107.42, only MTLa1 and MTLa2 PCR products were obtained indicating that these isolates are MTLa homozygotes; the other isolates were found to be heterozygous for MTL; (d) Candida metapsilosis isolates (1–6 referring to CBS 2315, CBS 107.47, CBS 109.07, CBS 111.27, CBS 1046, and CBS 2916), whereas only MTLα1 (150 bp) and MTLα2 (188 bp) PCR products were obtained with CBS 2315 indicating MTLα homozygosity; all MTL gene products were obtained for the other isolates showing that they are MTL heterozygous. M, Marker; NC, Negative control.