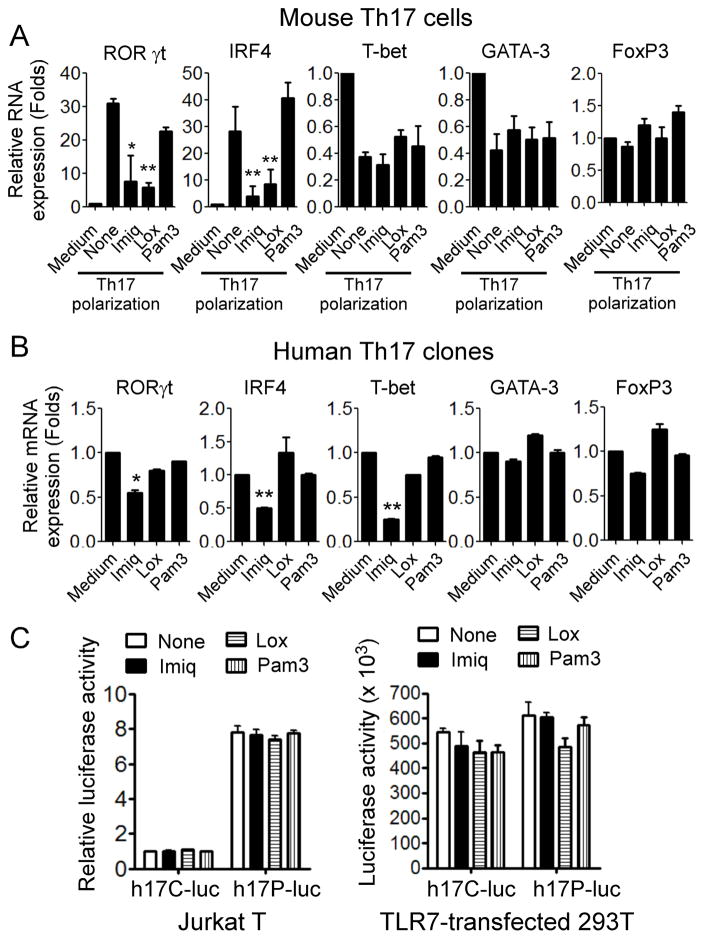
Figure 4. Inhibitory effect of TLR7 ligands on lineage-specific transcription factors in Th17 cells.
(A) TLR7 ligand Imiq and Lox inhibited the gene expression of RORγt and IRF4, but not T-bet, GATA-3 and FoxP3 in mouse CD4+ T cells cultured in Th17 polarization condition medium for 6 days. Relative mRNA expression level of each gene was determined by real-time PCR with specific primers, normalized to GAPDH expression and then adjusted to the level in naïve CD4+ T cells. Data shown are mean ± SD from three independent experiments, and paired t-test was performed. *p<0.05 and ** p<0.01, compared with none treatment group. (B) Imiq treatment inhibited RORγt, IRF4, and T-bet gene expression in human Th17 cells. Human Th17 cell clones were cultured in the presence of indicated TLR ligands for 24 hours, and gene expression levels of transcription factors were determined by real-time PCR. Relative mRNA expression level of each gene was normalized to GAPDH expression and then adjusted to the level in Th17 cells cultured in medium only. Data shown are mean ± SD from triplicate experiments, and paired t-test was performed. *p<0.05 and ** p<0.01, compared with the medium only group. (C) Treatment with TLR7 ligands did not affect IL-17 promoter activity. Jurkat T or 293T cells were transfected with either human IL-17 promoter-luciferase plasmid (h17P-Luc) or control luciferase vector (hp17C-Luc) for 24 hours and then treated with Imiq, Lox, or Pam3 for additional 24 hours. Luciferase activities were measured in cell lysates and normalized to the activity in cells only transfected with the empty vector. Results shown are mean ± SD from three independent experiments.