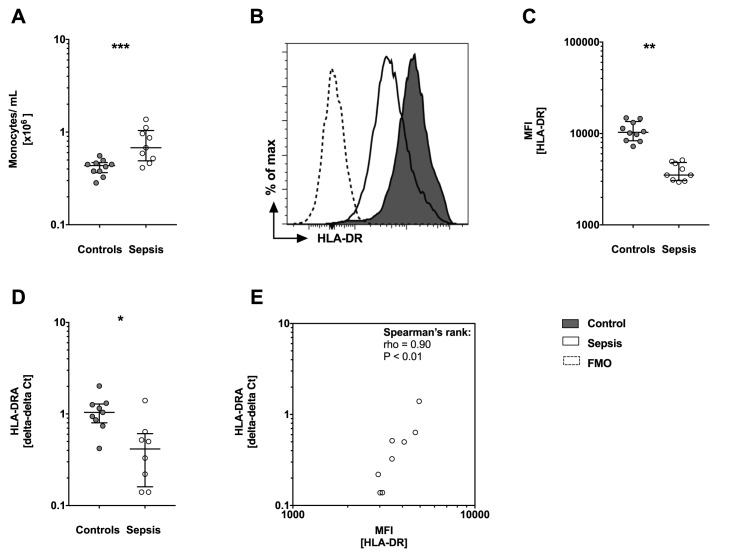
Fig 1. Monocytosis but loss of protein surface and gene expression of human leucocyte antigen DR (HLA-DR) is observed in sepsis patients.
(A) Number of monocytes in cells/mL shows significant higher numbers of monocytes/mL in sepsis patients (n = 9) compared to controls (n = 10). (B) Protein surface expression levels of HLA-DR by monocytes are shown as a representative histogram and (C) with the corresponding analysis of median fluorescence intensity (MFI). Sepsis patients show reduced HLA-DR surface expression compared to controls. (A-C) Whole blood was stained for cell surface molecules (CD14 and HLA-DR) and analyzed by flow cytometry (FACS). Data are presented as box and whisker plots with median and interquartile range and statistical analysis was performed using non-parametric Mann-Whitney-U test. (D) Gene expression of HLA-DRA is reduced in sepsis patients. mRNA was prepared from whole blood and HLA-DRA expression levels were assessed by quantitative PCR (qPCR). HLA-DRA expression levels are normalized to internal control gene peptidylpropylisomerase B (PPIB). Data are presented using the delta-delta Ct method and as box and whisker plots showing the median with interquartile range. Statistical analysis was performed using non-parametric Mann-Whitney-U test. (E) Spearman’s rank correlation is presented with median fluorescence intensity (MFI) for HLA-DR protein on the x-axis and mRNA expression of HLA-DR presented as delta-delta Ct on the y-axis. Each circle represents a data set from an individual patient. CD: cluster of differentiation, mRNA: messenger RNA, FMO: Fluorescence Minus One controls, PCR: polymerase chain reaction. P<0.05:*; P<0.01:**; P<0.001:***.