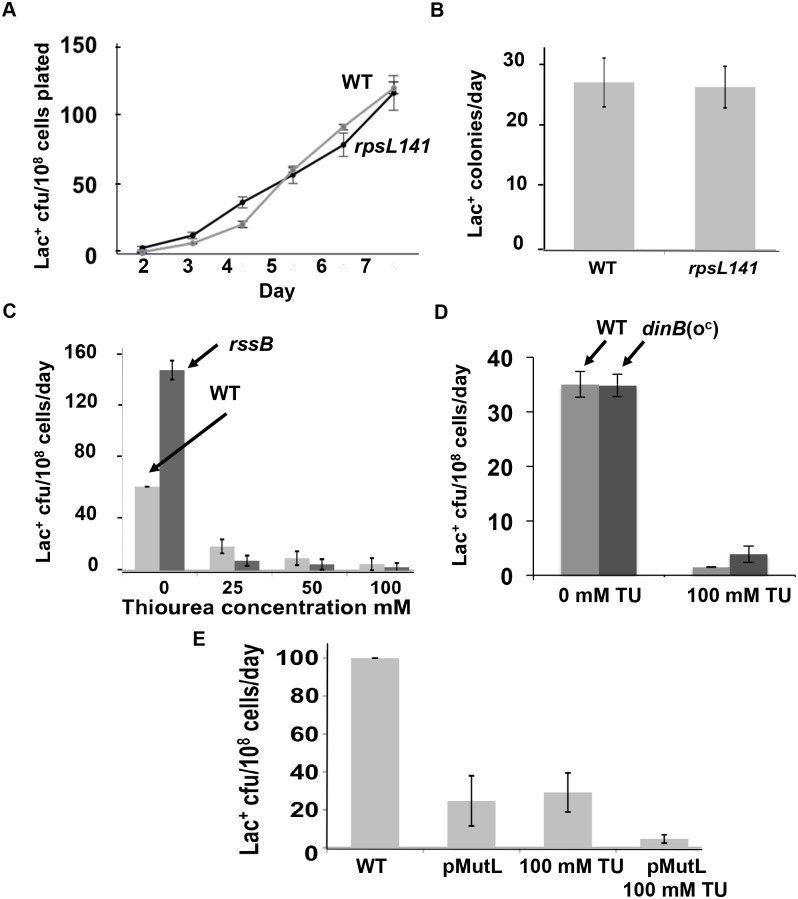
Fig 4. ROS promote MBR other than or in addition to by upregulation of the RpoS or SOS responses, oxidation of proteins, or saturation of mismatch repair.
(A, B) The hyper-accurate ribosomal protein allele rpsL141 [62] does not reduce MBR, implying that ROS promote MBR other than by producing carbonylated proteins, which are reduced by this allele. (A) Representative experiment. (B) Mean ± SEM of three experiments. (C) Artificial upregulation of RpoS levels in ΔrssB strains does not restore MBR in TU-treated cells, implying that ROS promote MBR other than or in addition to by upregulation of RpoS. (D) An operator-constitutive dinB(oc) allele, which substitutes for the SOS response in MBR [41], does not substitute for depletion of ROS by TU. (E) Over-expression of mutL, the limiting mismatch repair (MMR) component in MBR [63], causes additive reduction of MBR with TU treatment, implying that TU and MMR reduce MBR by different pathways, indicating that ROS promote MBR other than by saturation of MMR capacity. Strains used: wild type (WT) SMR4562; rpsL141, PJH3178 ΔrssB, SMR12566; dinB(oc) SMR10308; PBADMutL, SMR15378. PBADMutL was derepressed by absence of glucose in the medium.