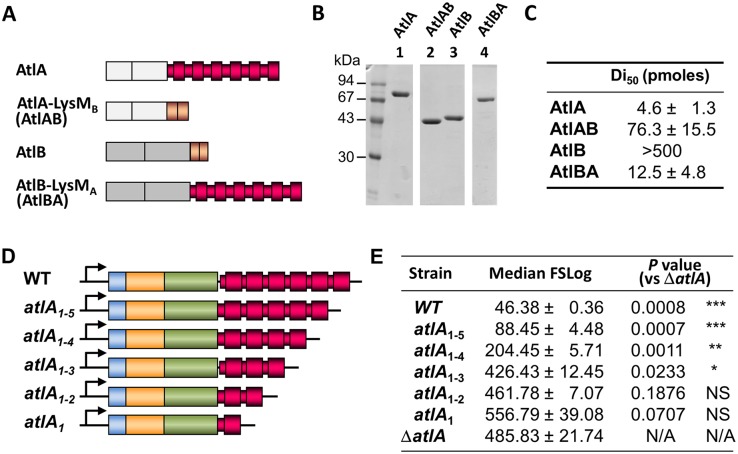
Fig 6. Contribution of the LysM domain to septum cleavage.
A. Schematic representation of AtlA and AtlB derivatives expressed and purified to test their septum cleavage activity. Full-length AtlA and AtlB (without signal peptides), as well as their counterparts with LysMB (AtlAB) or LysMA (AtlBA) domains, were expressed in E. coli. B. SDS-PAGE of AtlA (lane 1), AtlAB (lane 2), AtlB (lane 3) and AtlBA (lane 4) samples showing that all proteins were purified to homogeneity. C. Flow cytometry analysis of septum cleavage activity of recombinant proteins in vitro using OG1RF ΔatlA cell chains as a substrate (see materials and methods). The Di50 (Dechaining index) value corresponds to the amount of enzyme in pmoles that is able to decrease the median FSC value of ΔatlA cell chains by 50% in 15 minutes at 37°C. D. Schematic representation of atla locus in E. faecalis JH2-2 and isogenic derivatives producing AtlA with a C-terminal LysM domain containing a variable number of LysM repeats (6 in WT; 5 in atlA1-5; 4 in atlA1-4; 3 in atlA1-3; 2 in atlA1-2; 1 in atlA1). E. Comparison of median forward scattered (FSC) light values corresponding to the cell chain lengths of WT, atlA1-5, atlA1-4, atlA1-3, atlA1-2, atlA1 and ΔatlA strains. P values and significance corresponding to comparisons with the ΔatlA strain are indicated.