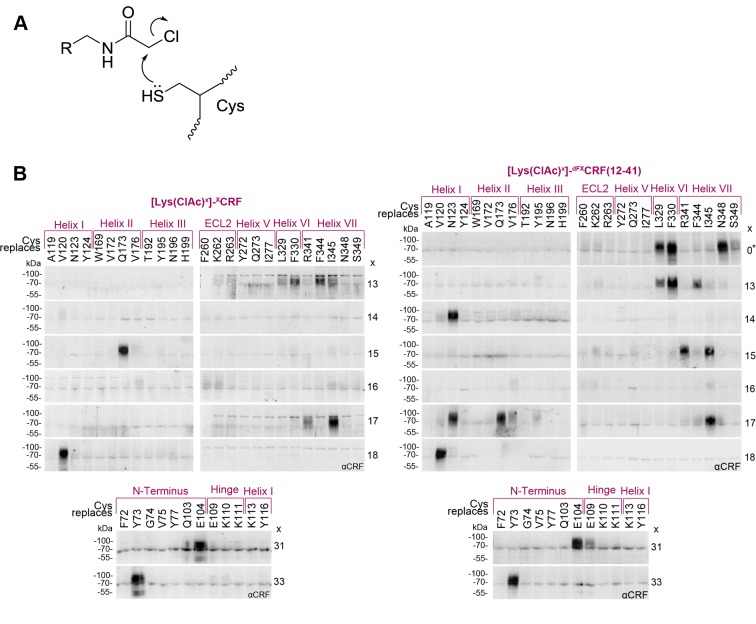
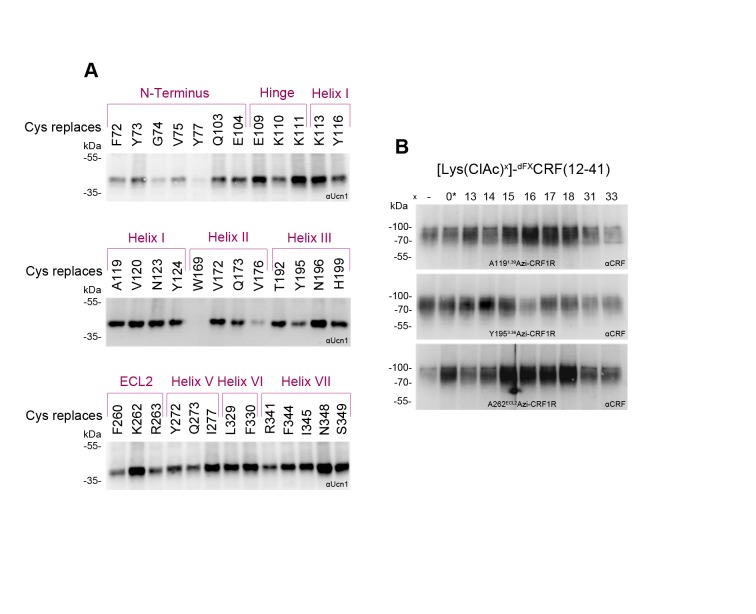
Figure 3. Cys-ClAc pair-wise crosslinking to pinpoint intermolecular pairs of proximal amino acids in ligand-CRF1R complexes.
(A) Nucleophilic substitution reaction between a cysteine (Cys) thiol and a α-chloroacetamide (ClAc) moiety. (B) Transiently transfected 293T cells expressing each Cys-CRF1R mutant were incubated with each of the ClAc-peptide ligands. The mutation site in CRF1R is indicated in the upper row. The positions of ClAc moiety in the ligands are indicated in the right column of each panel. The peptide indicated with a star (*) bears the ClAc not on the side chain of a Lys, but directly on the N-terminus (see Table 1). Whole-cell lysates were separated on 10% SDS-PAGEs and analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-CRF antibody. The non-deglycosylated ligand-CRF1R complex runs at an apparent molecular weight of ~70–100 kDa (Coin et al., 2013). The non-crosslinked ligand is not detected (MW ~3–4 kDa). Signals were considered as hits if their intensity was higher than a threshold defined as 50% of the most intense signal per ligand.