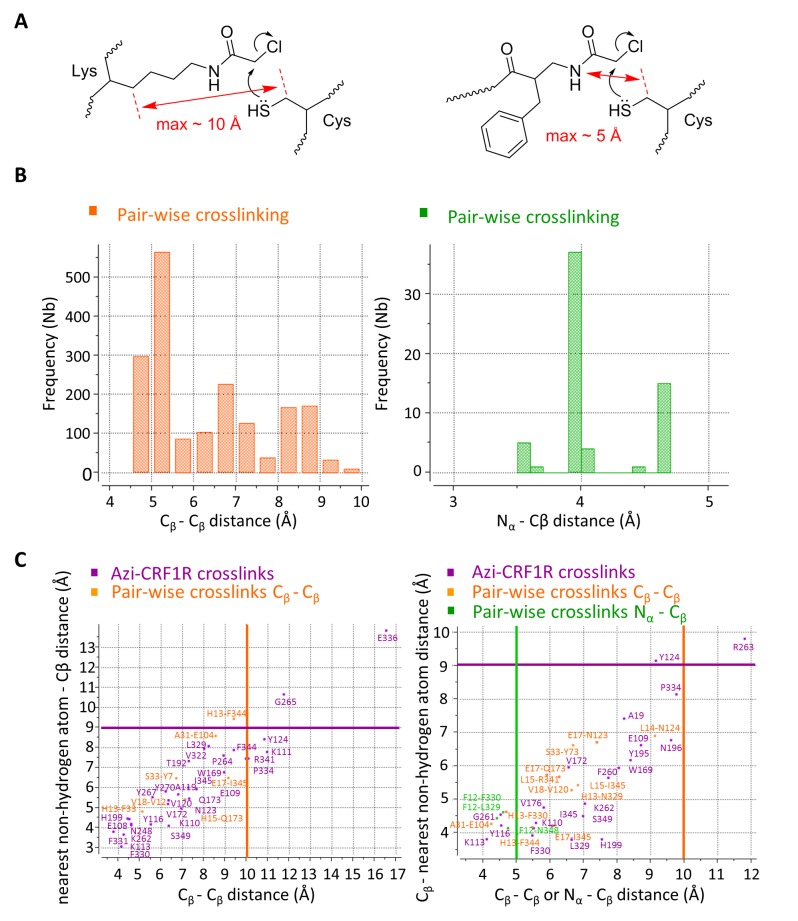
Figure 4. Atom-atom distances of residue pairs in the peptide-CRF1R complexes.
(A) Geometrical estimation of the Cβ-Cβ distance or N-Cβ distance for the ClAc-Cys reaction to happen when the ClAc moiety is installed on the side chain of a Lysine residue (left) or at the N-terminus of the peptide (right). (B) Range of sterically possible Cβ-Cβ distances (left) or N-Cβ distances (right) in the covalent crosslinked product for residues involved in pair-wise crosslinking. The distance range distributions were calculated based on the Monte Carlo sampling of the free molecule conformations in ICM software. (C) Measured distances for Azi photo-crosslinking and pair-wise chemical crosslinking hits between ligand and receptor in the predicted model of the CRF-CRF1R (left) and the dFXCRF(12-41)-CRF1R complex (right). For Azi photo-crosslinking hits (magenta), distances are measured from the Cβ atom of the indicated CRF1R residue to the nearest Cβ atom of CRF (x-axis) or to the nearest non-hydrogen atom of CRF (y-axis) or dFXCRF(12-41). For pairs of amino acids involved in chemical crosslinking, distances plotted along the x-axis are measured either as Cβ-Cβ (orange) or N-Cβ (green). The horizontal magenta line shows the approximate 9 Å radius for the reach of Azi crosslinking (from Cβ of Azi), vertical lines show the approximate 10 Å (orange) and 5 Å (green) cutoff for pair-wise crosslinking between Cβ-Cβ or N-Cβ, respectively.