Fig. 4.
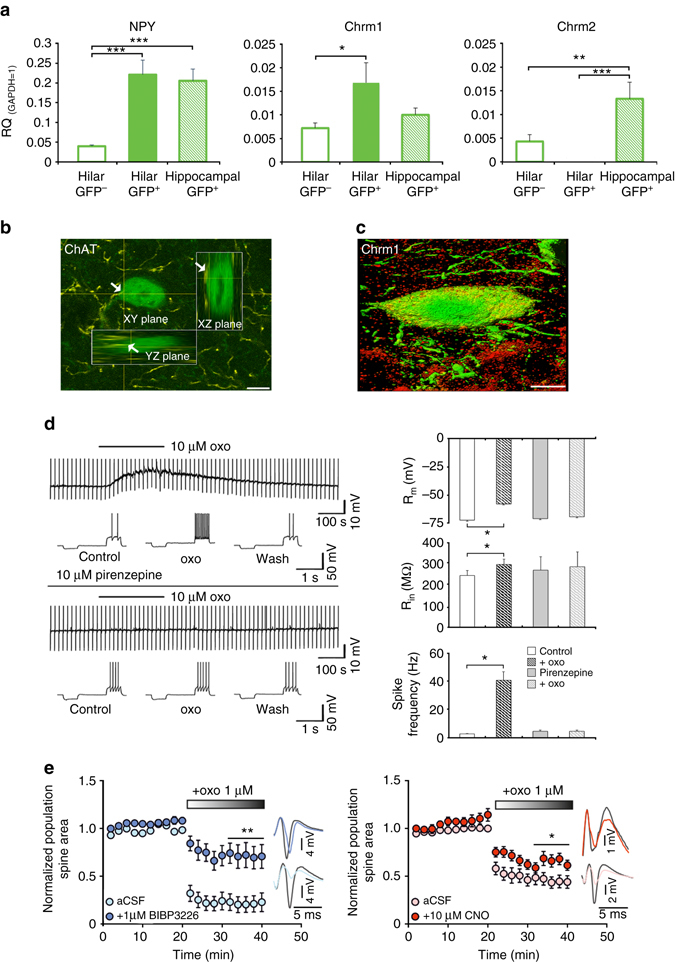
Chrm1 expression and function in HIPP cells. a Hilar GFP+ cells of NPY-GFP mice (n = 6–8) are enriched with mRNA for NPY and M1 muscarinic receptors (Chrm1) but not M2 receptor (Chrm2). Values are expressed relative to the housekeeping gene GAPDH. b A 3D-reconstruction of a GFP+ neuron targeted by cholinergic fibers (arrows) at the soma. Scale bar, 10 μm. c A GFP+ neuron (green) in the dorsal hilus of an NPY-GFP mouse with somatic immunolabeling of M1 receptors (red). Scale bar, 5 μm. d (Left) Representative current-clamp recording from GFP+ interneurons. Application of 10 µM oxotremorine M (oxo) induces a pirenzepine-sensitive transient depolarization paralleled by a significant increase in input membrane resistance and an increase in spike activity. (Right) Quantification of spike activity. Oxo induces a transient membrane depolarization from resting membrane potential in 7 out of 7 recorded neurons, paralleled by a significant increase in input membrane resistance and mean spike frequency elicited by positive current injections. These effects are abolished in the presence of the M1 receptor antagonist pirenzepine (10 μM; n = 5). e In field recordings, either Y1 receptor blockage (left) (n = 6 slices with BIBP3226 and n = 6 slices without BIBP3226) or pharmacogenetic HIPP cell inactivation (right) (n = 8 slices with BIBP3226 and n = 10 slices without BIBP3226) counteracts the depression of population spikes induced by oxo bath application. Example traces to the right of the graph illustrate the difference in response to perforant path stimulation. Values are means ± s.e.m. Statistical analysis was done with Fisher’s LSD following one-way ANOVA in a, Wilcoxon signed rank test in d and Student’s unpaired t-test in e. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
