Figure 1.
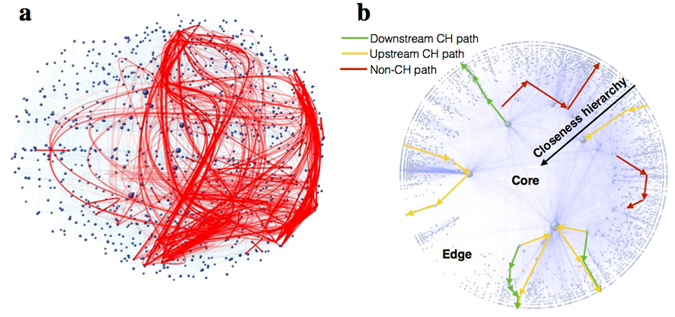
Empirical paths in the human brain (panel (a)) and the illustration of paths conforming to the policies identified by our measurements (panel (b)). A path is hierarchically conform (CH) if does not contain a large-small-large pattern forming a “valley” anywhere in its closeness centrality sequence (green and yellow paths in panel (b)). An upstream path contains at least one step towards the core of the network (yellow paths), while in downstream paths the closeness centrality monotonically decreases (green paths). The underlying faded network in panel (b) is only for illustration purposes, where smaller radial coordinate of a node indicates higher closeness centrality.
