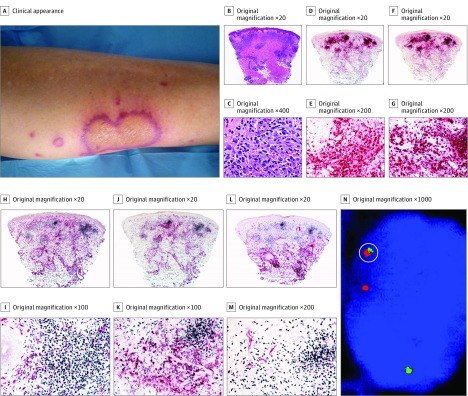
Figure 3. Histiocytoid Sweet Syndrome in a Patient With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Case 1).
A, Clinically, the lesions occurred on the lower extremities and were annular with an erythematous border. B and C, Hematoxylin-eosin–stained specimens. B, Histopathologic features consist of edema in the papillary dermis and a bandlike infiltrate in the superficial dermis; there are also perivascular infiltrates around deep dermal vascular plexus. C, At higher magnification, the predominant cells of the infiltrate are mononuclear cells with vesicular twisted nuclei and scant eosinophilic cytoplasm; nuclei are slightly pleomorphic, and there are some mitotic figures. D and E, Double immunostained specimens (myeloperoxidase [MPO, red] and CD163 [black]). D, Scanning power. E, At higher magnification, most cells express MPO, and very few cells at the periphery express CD163. F and G, Double immunostained specimens (MPO [red] and myeloid nuclear differentiation antigen [MNDA, black]). F, Scanning power. G, At higher magnification, most cells of the infiltrate coexpressed MNDA in their nuclei and MPO in their cytoplasm. H and I, Double immunostained specimens (MNDA [black] and CD163 [red]). H, Scanning power. I, At higher magnification, most cells of the infiltrate expressed MNDA in their nuclei, whereas some cells at the periphery expressed CD163 in their cytoplasm; no cells coexpress both markers. J and K, Double immunostained specimens(MNDA [black] and CD14 [red]). J, Scanning power. K, At higher magnification, the cells of the nodules express MNDA in their nuclei, whereas cells expressing CD14 in their cytoplasm are at the periphery of the nodules. L and M, Double immunostained specimens (MNDA [black] and CD34 [red]). L, Scanning power. M, At higher magnification, most cells of the infiltrate express MNDA in their nuclei, whereas only endothelial cells of the blood capillaries express CD34 in their cytoplasm. N, By fluorescent in situ hybridization, single scattered cells show red-green bcr/abl fusion signal (circled); these cells are interpreted as leukemia cells intermingled with nonneoplastic cells of histiocytoid Sweet syndrome.