Abstract
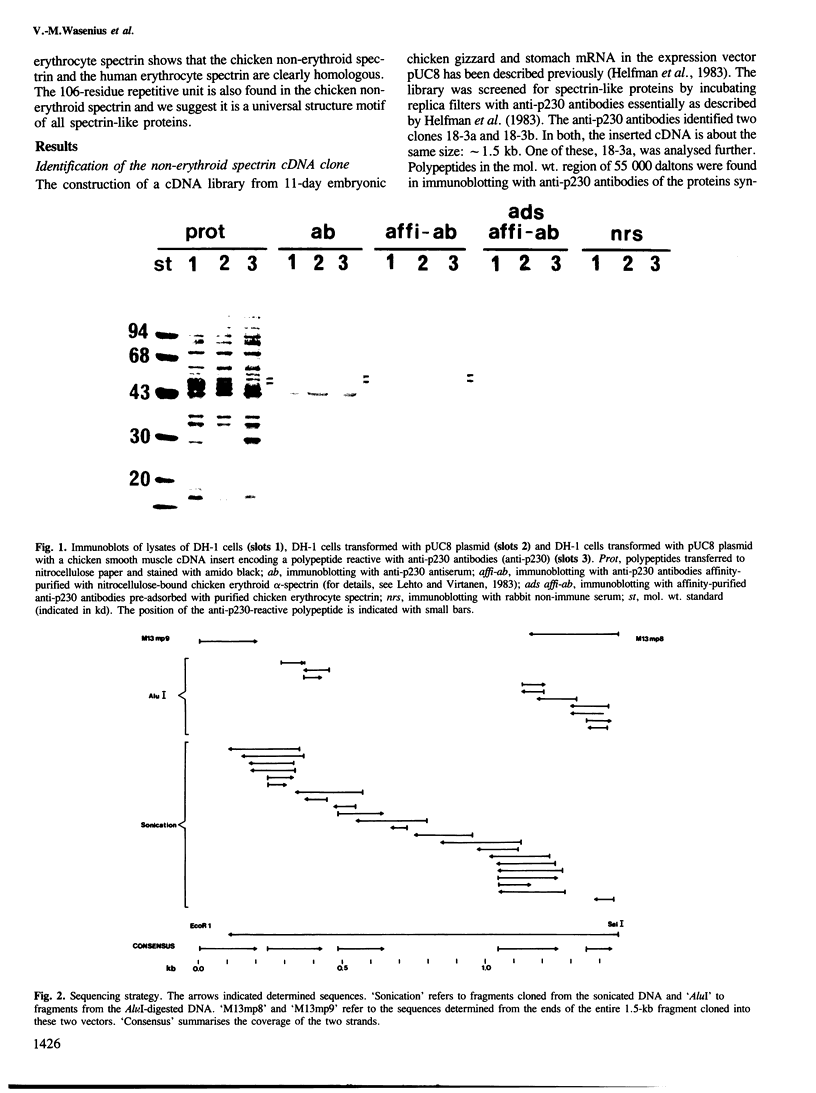
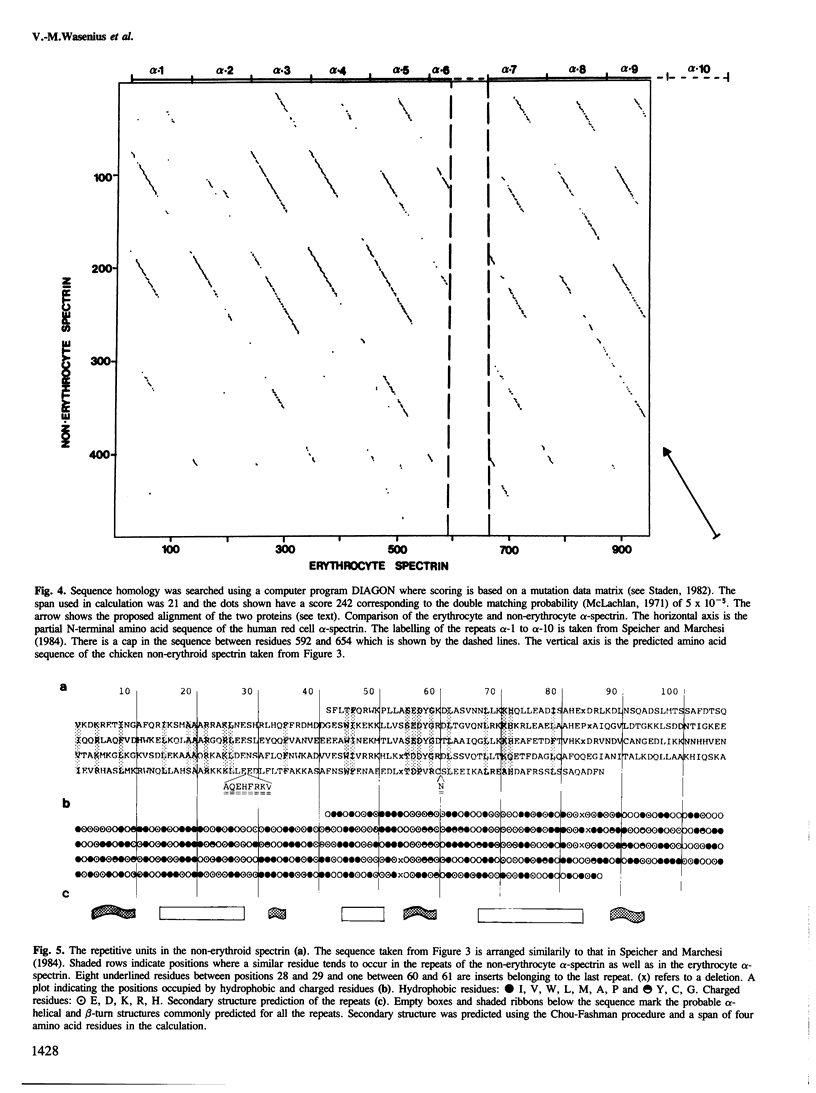
Immunological screening of a chicken gizzard cDNA expression library was used to isolate two clones encoding a part of the non-erythroid spectrin-like protein. Clones were identified by immunoblotting of the polypeptides synthesized in Escherichia coli cells transformed with cDNA cloned in the pUC8 plasmid vector using polyclonal rabbit antibodies raised against bovine non-erythroid spectrin. The sequence of an approximately 1.5-kb cDNA insert of one clone was determined. Analysis of the predicted amino acid sequence reveals that, despite differences in immunological cross-reactivity and peptide maps, the chicken non-erythroid and the human erythrocyte spectrins are highly homologous proteins. Like the human erythrocyte spectrin, the chicken smooth muscle spectrin appears also to be constructed from repeated, homologous structures of 106 amino acid residues. This is probably a universal structure motif of spectrins.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baines A. J. The spread of spectrin. Nature. 1983 Feb 3;301(5899):377–378. doi: 10.1038/301377b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Davis J., Fowler W. E. Brain spectrin, a membrane-associated protein related in structure and function to erythrocyte spectrin. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):126–131. doi: 10.1038/299126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett V., Stenbuck P. J. Association between ankyrin and the cytoplasmic domain of band 3 isolated from the human erythrocyte membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6424–6432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Cohen C. M., Tyler J. Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Kelly T., Mangeat P. Nonerythrocyte spectrins: actin-membrane attachment proteins occurring in many cell types. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):478–486. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlin R. K., Bartelt D. C., Siekevitz P. Identification of fodrin as a major calmodulin-binding protein in postsynaptic density preparations. J Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;96(2):443–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Empirical predictions of protein conformation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1978;47:251–276. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.47.070178.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C. M. The molecular organization of the red cell membrane skeleton. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):141–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Comparison of spectrin isolated from erythroid and non-erythroid sources. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):529–539. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08498.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Fodrin is the general spectrin-like protein found in most cells whereas spectrin and the TW protein have a restricted distribution. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90383-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P., Osborn M., Weber K. An F-actin- and calmodulin-binding protein from isolated intestinal brush borders has a morphology related to spectrin. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):843–854. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P. Spectrin, fodrin, and TW260/240: a family of related proteins lining the plasma membrane. Cell Motil. 1983;3(5-6):671–682. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P., Weber K. Erythroid spectrin, brain fodrin, and intestinal brush border proteins (TW-260/240) are related molecules containing a common calmodulin-binding subunit bound to a variant cell type-specific subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4002–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P., Weber K. Mapping the fodrin molecule with monoclonal antibodies. A general approach for rod-like multidomain proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 25;167(2):275–293. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Shiffer K. The spectrin membrane skeleton of normal and abnormal human erythrocytes: a review. Am J Physiol. 1983 Mar;244(3):C121–C141. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.244.3.C121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Zagon I. S., Kulikowski R. R. Identification of a spectrin-like protein in nonerythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7570–7574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman S. R., Zagon I. S., Whitfield C. F., Casoria L. A., McLaughlin P. J., Laskiewicz T. L. A spectrin-like protein from mouse brain membranes: immunological and structural correlations with erythrocyte spectrin. Cell Motil. 1983;3(5-6):635–647. doi: 10.1002/cm.970030528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Fiddes J. C., Thomas G. P., Hughes S. H. Identification of clones that encode chicken tropomyosin by direct immunological screening of a cDNA expression library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Feramisco J. R., Ricci W. M., Hughes S. H. Isolation and sequence of a cDNA clone that contains the entire coding region for chicken smooth-muscle alpha-tropomyosin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14136–14143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Nelson W. J. Expression of spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):505–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E., Nelson W. J., Kasamatsu T. Segregation of two spectrin forms in the chicken optic system: a mechanism for establishing restricted membrane-cytoskeletal domains in neurons. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Virtanen I. Immunolocalization of a novel, cytoskeleton-associated polypeptide of Mr 230,000 daltons (p230). J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):703–716. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine J., Willard M. Fodrin: axonally transported polypeptides associated with the internal periphery of many cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):631–642. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchesi V. T. Spectrin: present status of a putative cyto-skeletal protein of the red cell membrane. J Membr Biol. 1979 Dec 14;51(2):101–131. doi: 10.1007/BF01869164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Tests for comparing related amino-acid sequences. Cytochrome c and cytochrome c 551 . J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):409–424. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90390-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow J. S., Speicher D. W., Knowles W. J., Hsu C. J., Marchesi V. T. Identification of functional domains of human erythrocyte spectrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6592–6596. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. M., Christensen H. B. The William Osler lecture series. Continuing medical education in letters and science. JAMA. 1982 Apr 9;247(14):1983–1984. doi: 10.1001/jama.247.14.1983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Avian lens spectrin: subunit composition compared with erythrocyte and brain spectrin. J Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;97(4):1271–1276. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Lazarides E. Switching of subunit composition of muscle spectrin during myogenesis in vitro. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):364–368. doi: 10.1038/304364a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repasky E. A., Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Widespread occurrence of avian spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):821–833. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90444-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Davis G., Marchesi V. T. Structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. II. The sequence of the alpha-I domain. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14938–14947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speicher D. W., Marchesi V. T. Erythrocyte spectrin is comprised of many homologous triple helical segments. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):177–180. doi: 10.1038/311177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. An interactive graphics program for comparing and aligning nucleic acid and amino acid sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2951–2961. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Badley R. A., Paasivuo R., Lehto V. P. Distinct cytoskeletal domains revealed in sperm cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1083–1091. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altschuh D., Moras D., Bloomer A. C., Mondragon A., Klug A., Van Regenmortel M. H. Correlation between segmental mobility and the location of antigenic determinants in proteins. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):123–126. doi: 10.1038/311123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




