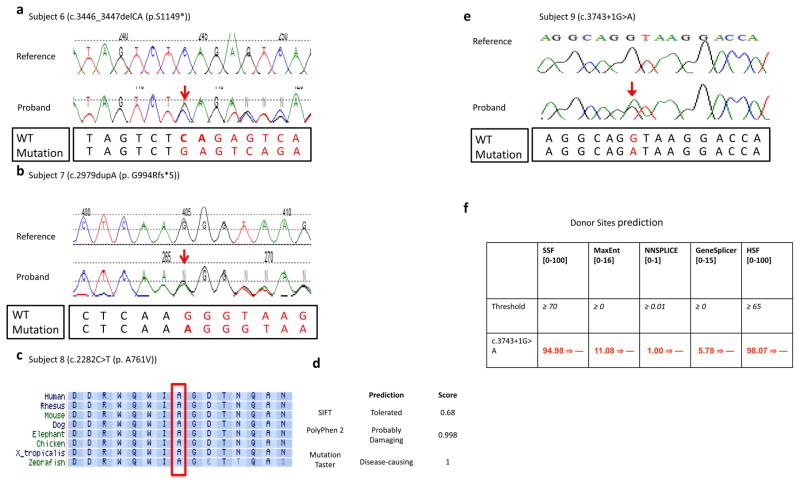
Figure 3.
(a,b) Sanger sequencing traces from subject 6 and subject 7 are presented. The WT and mutation sequences are shown separately below the Sanger traces. (c) Alignment of the TRIP12 protein sequence from multiple species around amino acid position 761 (NM_004238) that was altered from alanine to valine in subject 8. This alanine at position 761 was well conserved from human to zebrafish, and this missense change was predicted to be deleterious/disease-causing by MutationTaster and Polyphen-2 (d). (e) Chromatogram of de novo variant c.3743+1G>A and (f) results of in silico analysis of the 3743+1G>A variant found in subject 9 using five splicing prediction tools included in Alamut v2.7. The numbers in brackets indicate the value range generated by each predication tool. The threshold used by each prediction tool indicates that above this threshold the positions are predicted to be true splice-sites. The numbers in red are the actual value calculated by each prediction algorithm. All five prediction tools suggested that the donor splice site was abolished at the variant position.