Figure 1. Co-opted DNA repair during antibody diversification, and its significance in generating autoantibodies.
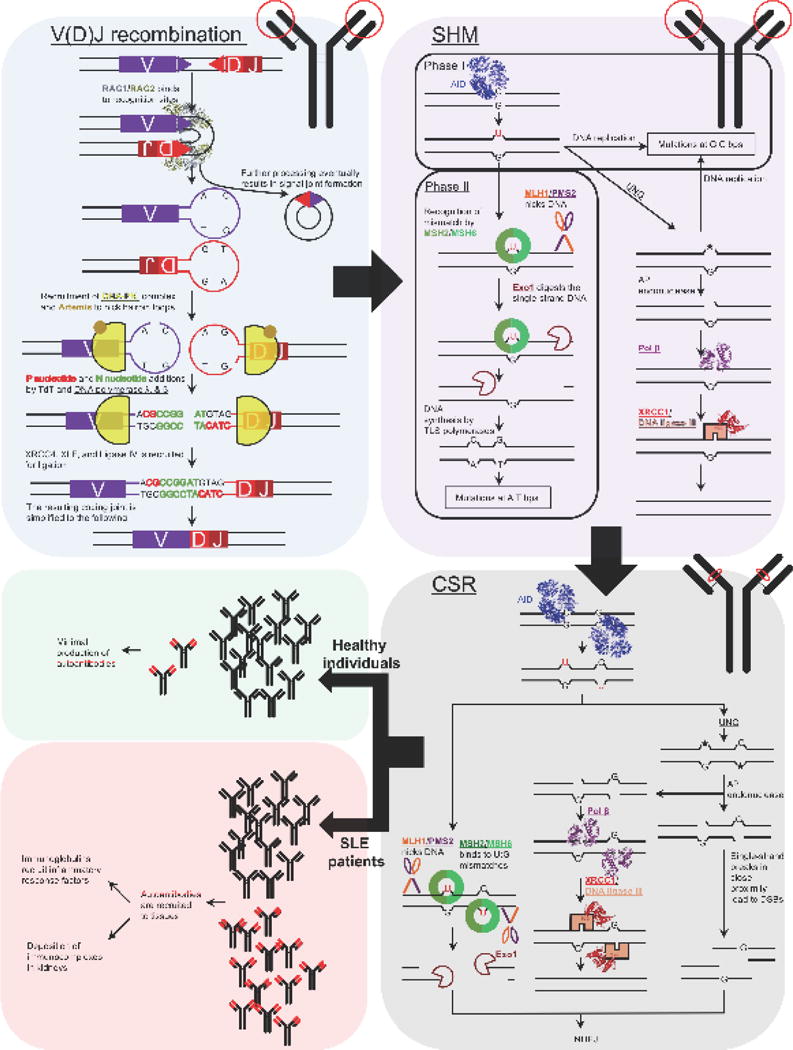
The three major processes for antibody diversification are V(D)J recombination, SHM, and CSR. The location of these processes are shown respective to the antibody (circled in red) pictured in the upper right corner of each box. Additionally, DNA repair proteins are underlined. During V(D)J recombination of the immunoglobulin heavy chain, RAG1 and RAG2 bind to recognition signal sequences (purple and red triangles) bringing the V and DJ sequences to close proximity to each other. RAG1/RAG2 create DSBs resulting in hairpin loops. The hairpin loops recruit Ku70/Ku80 and the DNA-PKcs (DNA-PK complex), and in coordination with Artemis, the hairpin DNA is nicked. This can create DNA overhangs that are filled in with P nucleotides and additional N nucleotides. Collectively, DNA synthesis at these sites is performed by the concerted activity of Polλ, Pol β, and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) in the immunoglobulin heavy chain. Afterwards, the ends are ligated by XRCC4, XLF, and ligase IV. SHM occurs in the variable region of the immunoglobulin gene. AID converts deoxycytidine to deoxyuridine, which can be processed by the UNG glycosylase to create an abasic site (★). During phase I of SHM, DNA replication of the deoxyuridine- or abasic site-containing DNA results in mutations at G:C bps. Conversely, the abasic site can be repaired by BER. In phase II of SHM, MMR processes the U:G mismatches leading to DNA gap-filling by TLS polymerases, which is in contrast to canonical MMR where DNA synthesis is performed by replicative DNA polymerases. The infidelity of the TLS polymerases results in mutations in A:T bps. CSR is similar to SHM; however, this occurs only at switch regions located downstream of the recombined VDJ regions of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. In this case, the intermediates of MMR and BER can result in single-strand breaks, and if they are in close proximity to each other, can lead to DSBs. The DSBs are resolved by NHEJ resulting in an immunoglobulin isotype switch. Aberrant DNA repair can possibly lead to increased production of pathogenic autoantibodies and the disease phenotypes present in SLE patients as shown in the lower left panel. PDB: RAG1/RAG2 (3JBX), AID (5JJ4), Pol β (5TB8), and XRCC1 (3PC8).
