Figure 3.
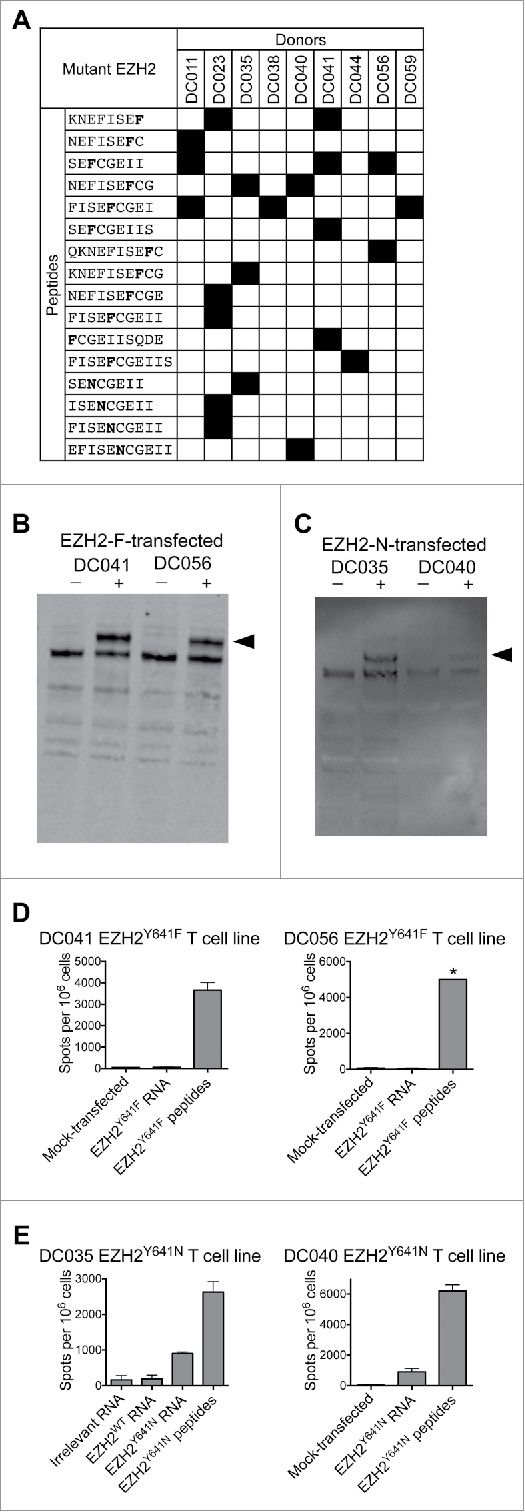
T cells from healthy donors recognize mutant EZH2 peptides and full-length EZH2Y641N. Healthy donor T cell lines derived from in vitro stimulation with the EZH2Y641F or EZH2Y641N peptide libraries were screened by IFNγ ELISPOT for reactivity against each individual peptide and against B cells expressing full-length EZH2. (A) Summary of minimal epitopes recognized by T cells. The minimal epitope was defined as the shortest peptide with the strongest response of all peptides tested. Mutant residues are indicated in bold font. (B–E) Autologous CD40-activated B cells were transfected with ivtRNA encoding full-length EZH2 and used to stimulate T cell lines. (B, C) Western blots demonstrating expression of EZH2 by B cells transfected with (B) EZH2Y641F or (C) EZH2Y641N. Although the staining is weak in panel C, the results were reproducible in independent experiments. (D, E) ELISPOT results for (D) EZH2Y641F or (E) EZH2Y641N-specific T cells (1–1.5 × 105 cells/well) incubated with B cells (2 × 105/well) that had been pulsed with peptides or transfected with ivtRNA. (D) T cell lines from DC041 and DC056 did not recognize processed EZH2Y641F, whereas (E) T cell lines from DC035 and DC040 did recognize processed EZH2Y641N. These ELISPOT results are from the same experiments shown in panels B and C. * = TNTC. All data are representative of at least 2–3 independent experiments.
