Figure 1.
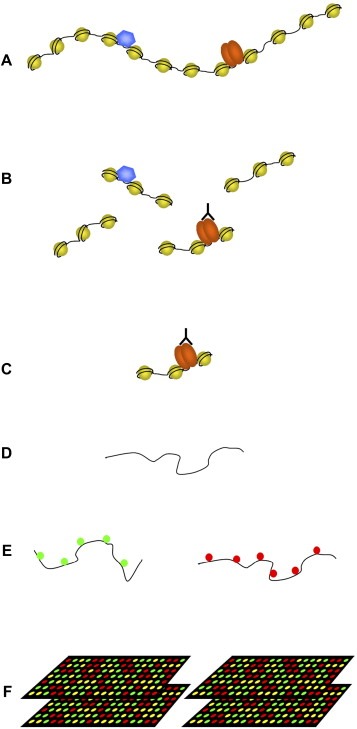
Overview of ChIP‐chip. (A) Using formaldehyde protein–protein and protein–DNA are cross‐linked in vivo. The cross‐linked chromatin is subsequently isolated. (B) The isolated chromatin is sheared in smaller fragments by sonication yielding fragments of 500–1000bp. The protein or histone modification of interest is precipitated using an antibody. The cross‐linked DNA is co‐precipitated. (C) The unbound chromatin is washed away. (D) The cross‐linking is reversed and the DNA is isolated. The DNA is amplified by either LM‐PCR or T7 linear amplification of DNA. (E) Total genomic DNA and ChIP DNA are differently labeled with Cy3 and Cy5. (F) Labeled DNA is hybridized on promoter arrays or arrays spanning the total non‐repetitive genome.
