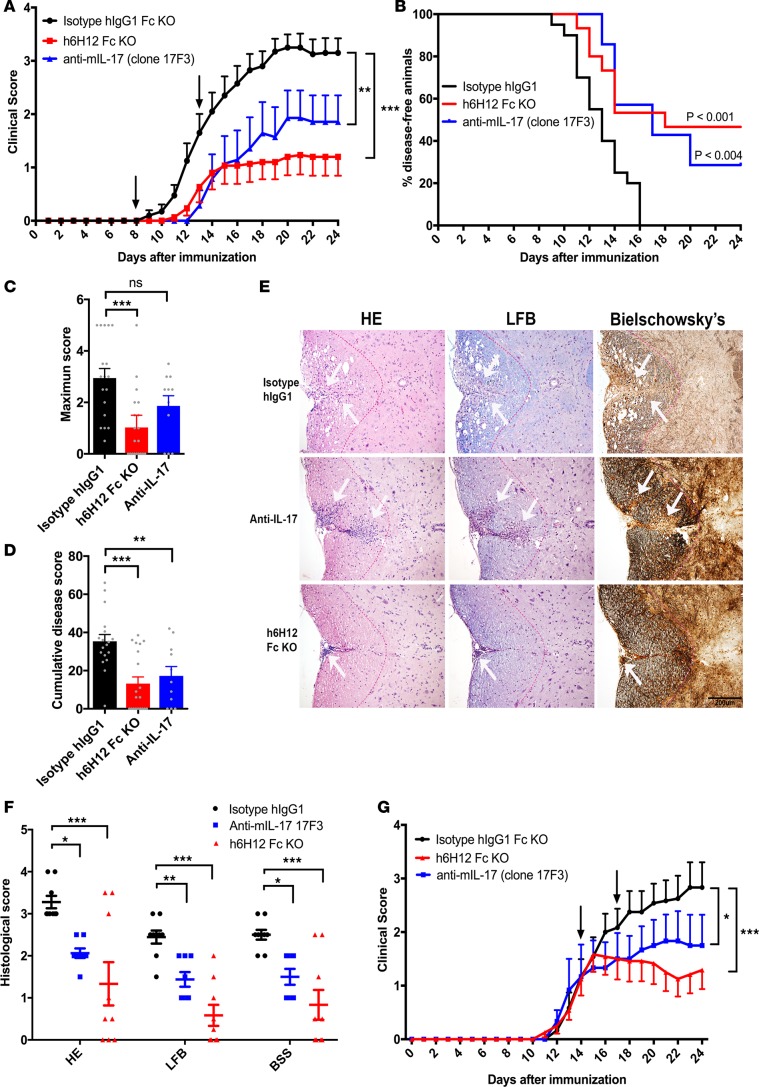
Figure 3. Anti-hCCR6 mAb prevents and inhibits EAE in hCCR6-Tg/mCCR6–/– mice.
(A) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) preventive study. Blockade of human CCR6 (hCCR6) with humanized 6H12 (h6H12) mAb (2 mg/kg, black arrows) prevents the development of EAE in hCCR6-Tg/mCCR6–/– mice immunized with recombinant mouse (rm) myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein (MOG). (B) Kaplan–Meier plot of the proportion of disease-free animals after EAE induction in isotype (n = 18, black line) versus h6H12 Fc-KO–treated (n = 20, red line) and anti–mIL-17 mAb–treated animals (n = 11, blue line) (Mantel-Cox log-rank test). (D) Maximum and (C) cumulative disease scores in isotype- (n = 18), h6H12 Fc-KO– (n = 20), and anti–mIL-17 mAb–treated mice (n = 11). (E) Representative stained histological sections of spinal cords from immunized animals treated with isotype control (top panels), h6H12 Fc-KO (middle panels), or anti–mIL-17 (bottom panels). Serial sections were stained with H&E to determine the degree of inflammatory cell infiltrates, luxol fast blue (LFB) to establish myelin integrity, and Bielschowsky silver stain (BSS) to ascertain axonal loss and damage (white arrows indicate area of leukocyte infiltration). Scale bar: 200 μm. (F) Histological scores for inflammation (H&E), demyelination (LFB), and axonal damage (BSS) (blacks bars, isotype control [n = 9]; blue bars, anti–mIL-17 [n = 8]; red bars, h6H12 Fc-KO [n = 9]). (G) EAE therapeutic study. Injections of h6H12 (5 mg/kg; black arrow) significantly reduce the disease development (n = 12, red curve) compared with mice treated with an isotype control mAb (n = 12, black curve) or anti–mIL-17 mAb (n = 8, blue curve). The clinical course of EAE (A and G) was analyzed with the nonparametric Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA with the Dunn’s post-hoc test. Histological, maximum clinical, and cumulative scores (C, D, and F) were compared by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test relative to the control isotype–treated group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.