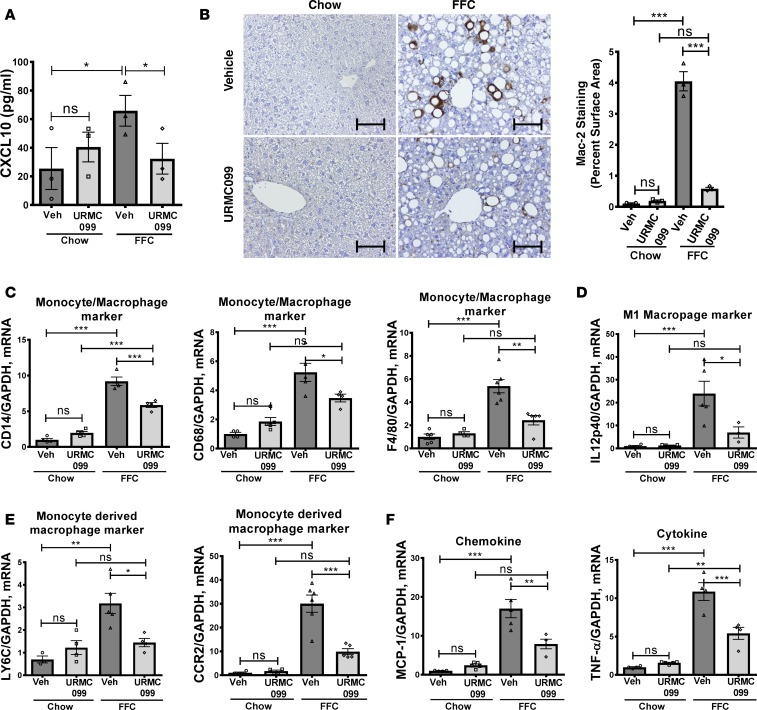
Figure 4. URMC099-treated mice have reduced FFC diet–induced macrophage-associated liver inflammation.
WT C57BL/6J mice were fed either chow or a diet high in saturated fat, fructose, and cholesterol (FFC) for 24 weeks, and URMC099 or vehicle (Veh) was given during the last 2 weeks. (A) CXCL10 levels in the serum were assessed by ELISA (n = 3). (B) Macrophage infiltration was evaluated by immunohistochemistry for macrophage galactose-specific lectin (Mac-2) antigen; Mac-2 staining was quantified in 10 random ×20 microscopic fields and averaged for each animal (n = 3) by morphometry using ImageJ software. Scale bars: 50 μm. Total RNA was extracted from liver tissue. The mRNA expression of (C) general monocyte and macrophage markers CD14, CD68, and F4/80 (n = 4–6), (D) M1 macrophage marker IL-12p40 (n = 4–5), (E) markers associated with monocyte-derived infiltrating macrophages CCR2 and LY6C (n = 4–5), and (F) the chemokine MCP-1 and the cytokine TNF-α were assessed by real-time PCR (n = 4–5). Fold change was determined after normalization to GAPDH expression in liver tissue, and expressed relative to that observed in chow-fed, vehicle-treated mice. Data represent mean ± SEM. Differences between the groups were compared using 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. ns, non-significant.