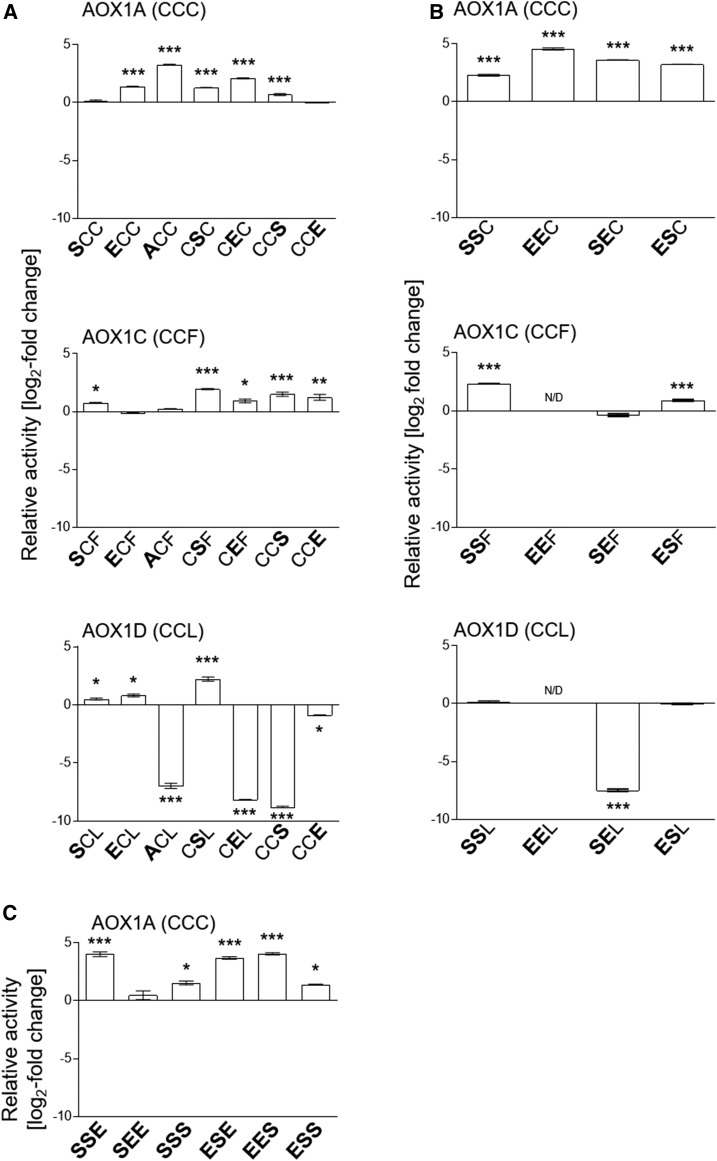
Figure 2.
Effects of amino acid substitutions on AOX activities. AOX isoenzymes with different single (A), double (B), or triple (C) substitutions of CysI, CysII, and/or CysIII (PheIII or LeuIII) were heterologously expressed in E. coli strain BHH8 and analyzed for oxygen consumption in isolated membrane vesicles under reducing conditions. As a basis for specific AOX activity, respiration rates were normalized for each sample using densitometry on immunoblots (Selinski et al., 2016). Graphed values (log2 fold change; mutant/wild type) represent averages from two to five independent protein induction experiments with the appropriate se. Asterisks indicate that the differences (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001) between the basal activities of wild-type protein and the activities of substituted AOX derivatives are statistically significant as determined by one-way ANOVA with posthoc Tukey’s honestly significant difference (HSD) test. Wild types are as follows: AOX1A, CCC; AOX1C, CCF; and AOX1D, CCL. Substitutions are presented in the one-letter code for amino acids in enlarged boldface letters.