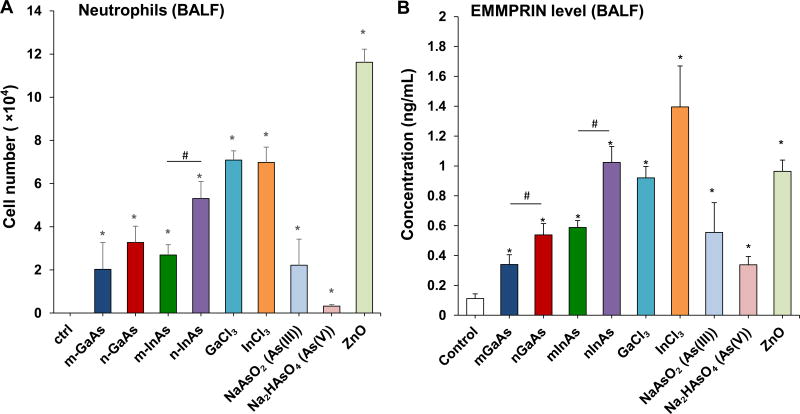
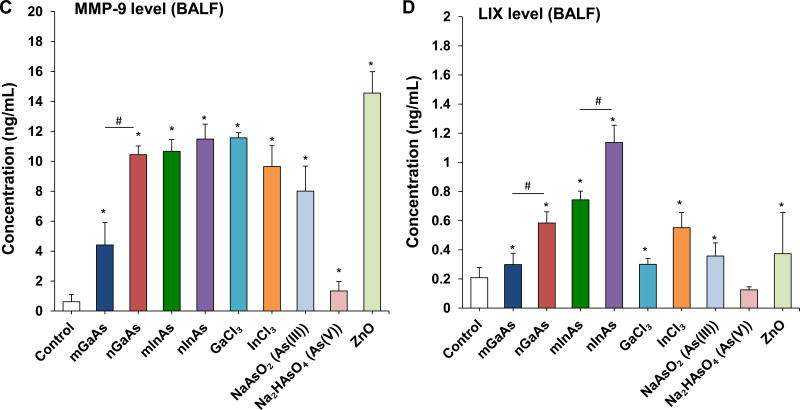
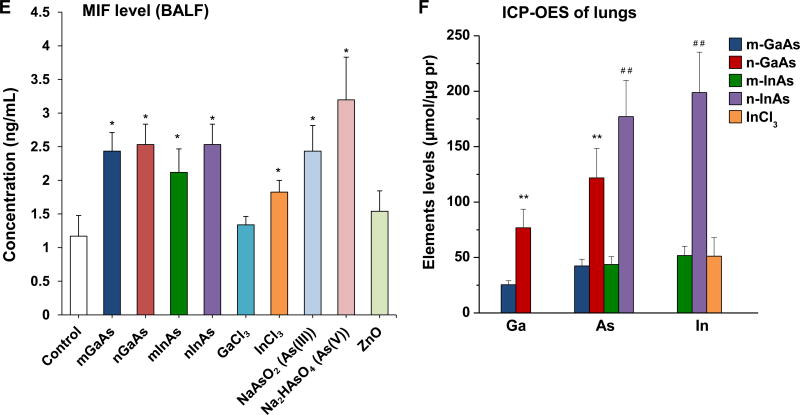
Figure 4.
Acute pulmonary effects of III-V materials in mice after exposure for 40 h. Anesthetized C57BL/6 mice were exposed to III-V particles and ionic forms by a one-time oropharyngeal aspiration of 0.014 mmol/kg (=2 mg/kg GaAs). The corresponding mass doses are listed in Table 3. There were 6 mice per group. Mice were euthanized after 40 h and BALF was collected to determine (A) neutrophil cell counts, (B) EMMPRIN, (C) MMP-9, (D) LIX and (E) MIF levels. (*) p < 0.05 compared to control. (#) p < 0.05 compared to nano-sized III-V particles. (F) Uptake of III-V materials in the lung tissue was reflected by ICP-OES analysis of Ga, As and In levels, normalized for protein content. The intact lungs were collected and digested by concentrated nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide before determining the elemental content by ICP-OES. No III-V element was detected in the lung tissues of animals exposed to ionic GaCl3, As(III) and As(V). (**) p < 0.05 compared to m-GaAs. (##) p < 0.05 compared to m-InAs.