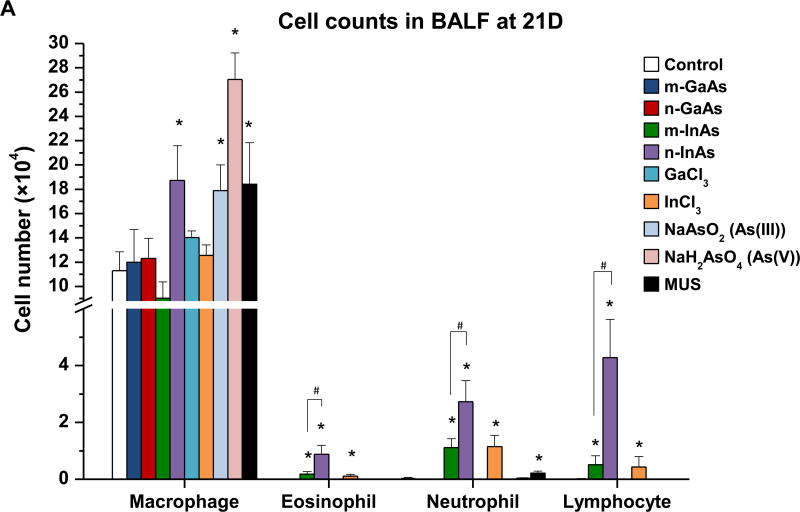
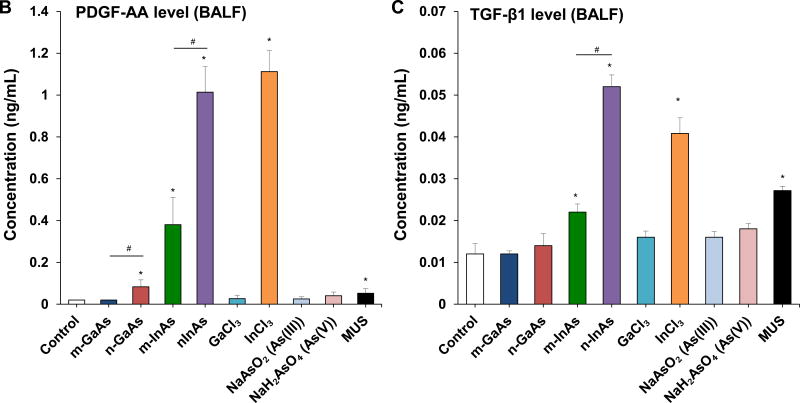
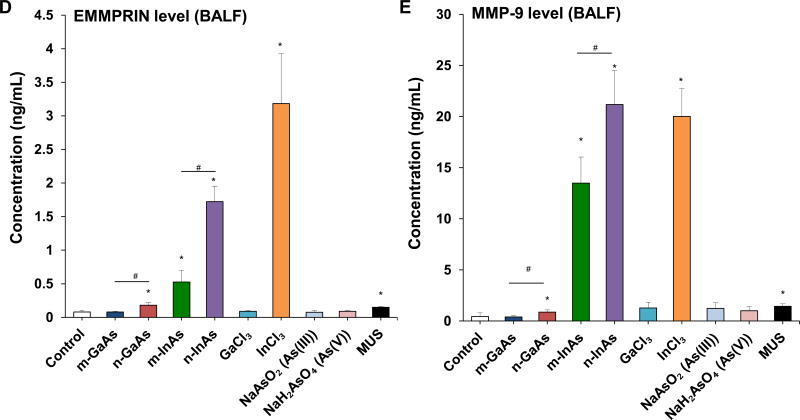
Figure 6.
Assessment of sub-acute lung injury potential of III-V materials in the murine lung, 21 D after initial exposure. The experiment was performed similar to the methods in Figure 4, except that the mice were sacrificed 21 D after the oropharyngeal aspiration of III-V particles and ionic forms at a dose of 0.014 mmol/kg (=2 mg/kg GaAs). The corresponding mass doses are listed in Table 3. The BALF was collected to assess (A) differential cell counts, including macrophages, eosinophils, neutrophils and lymphocytes, (B) pro-fibrogenic PDGF-AA and (C) TGF-β1 levels by ELISA. (D) EMMPRIN and (E) MMP-9 levels were also assessed by ELISA. MUS served as a positive control. (*) p < 0.05 compared to control. (#) p < 0.05 compared to nano-sized III-V particles.