Figure 2. Illustration of stable isotope labeling and quantitative MS.
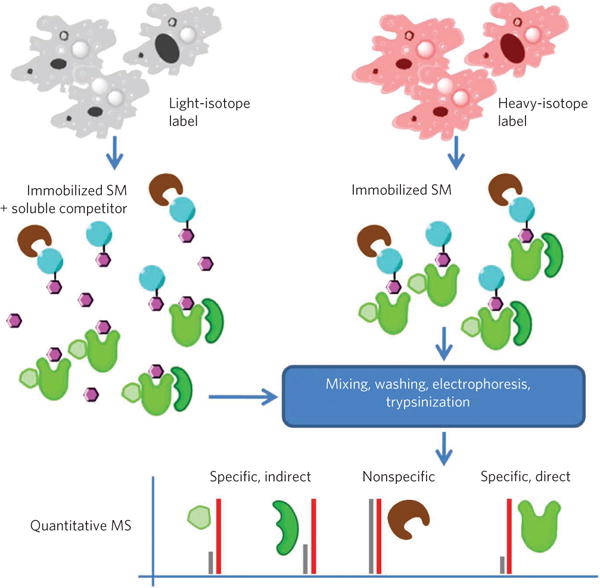
Cells are labeled with either heavy- or light-isotope labels. One sample is exposed to bead-immobilized small molecules (SM) in the presence of soluble competitor compound and the other in the absence of competitor. Following mixing, washing and electrophoresis, samples are digested using trypsin and peptide fragments analyzed by quantitative MS49. Ratios of heavy- and light-labeled peptides are used to determine specificity of interactions for the small molecule, potentially including both direct and indirect targets (for example, members of complexes including the direct target), but not to differentiate them.
