Figure 4. Illustrations of RNAi-based methods for target-identification and mechanism-of-action studies.
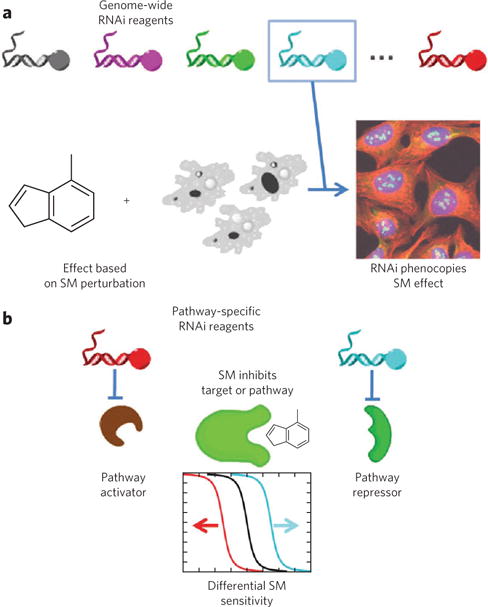
(a) In one implementation, phenotypes from genome-wide RNAi are compared to those induced by a small molecule (SM) of interest; full or partial phenocopy of the small-molecule effect by RNAi provides evidence that the gene product is a small-molecule target92. (b) When prior evidence suggests a particular target pathway, focused sets of RNA reagents can help to generate mechanistic hypotheses. In general, RNAi can enhance or suppress small-molecule effects, as in genetic epistasis analysis; in practice, more complex relationships among proteins than those illustrated may also exist93.
