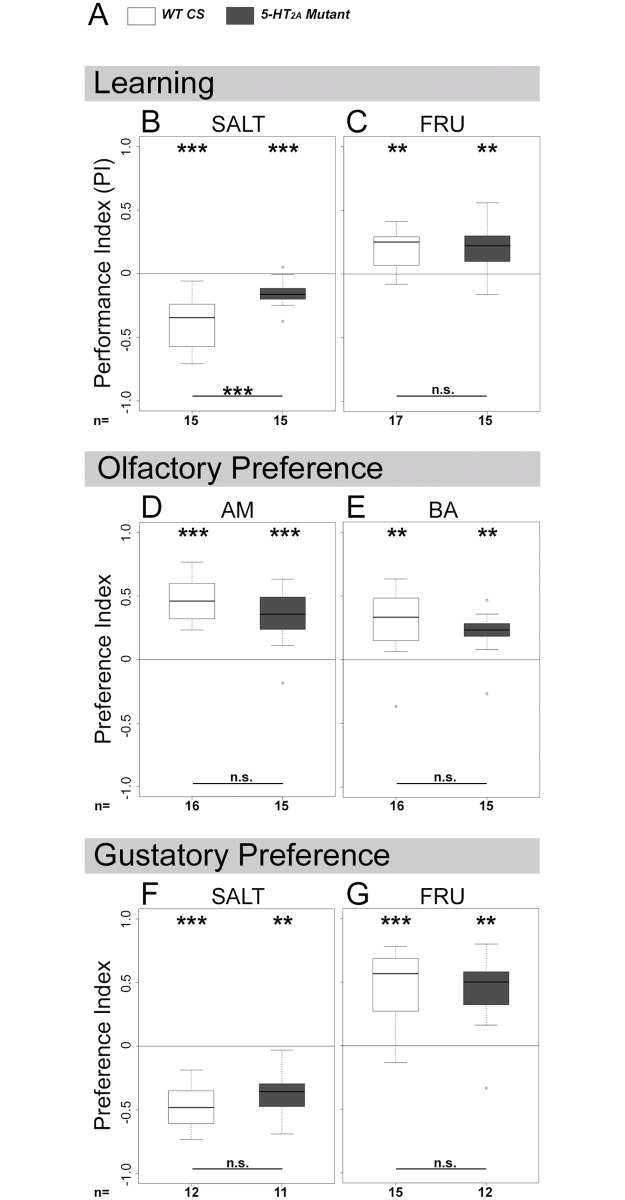
Fig 4. Impaired 5-HT2A receptor function throughout development impairs aversive olfactory learning and memory.
Homozygous 5-HT2A receptor gene mutants and wild-type control larvae (WT CS) were used to analyze aversive (B) and appetitive (C) olfactory learning and memory, olfactory amyl acetate (AM, in D) and benzaldehyde (BA in E) preferences and gustatory sodium chloride (SALT, in F) and fructose (FRU, in G) preferences. (A) provides a color scheme for the two different groups used in each experiment. Whereas mutant larvae showed olfactory and gustatory preferences as well as appetitive olfactory learning and memory comparable to WT CS larvae, aversive olfactory learning and memory was significantly reduced. Sample size (n = 11–17) is indicated at the bottom of each box plot. Differences against zero are given at the top of each box plot. Differences between mutant and wild type larvae are shown at the bottom of the panel. *** (p < 0.001), ** (p < 0.01), * (p < 0.05), n.s. (not significant p ≥ 0.05).