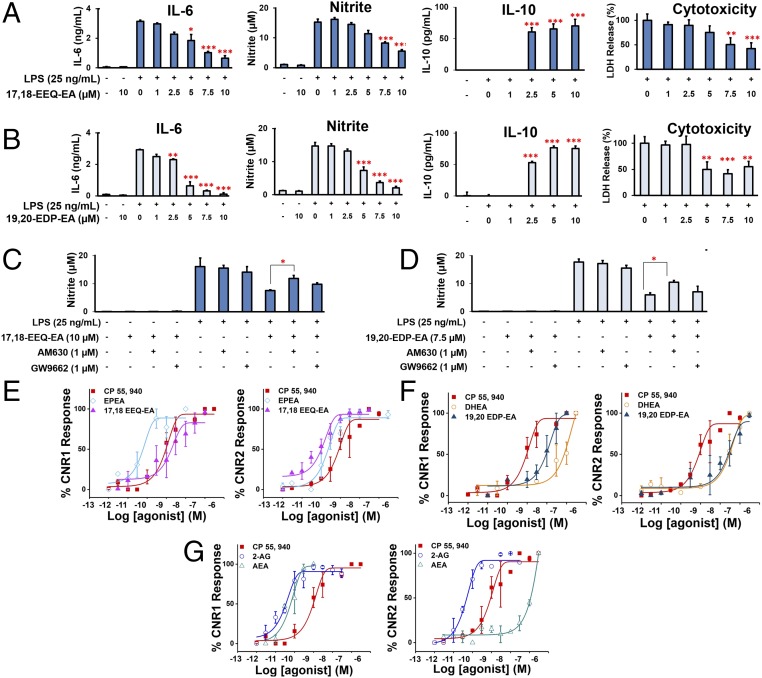
Fig. 4.
Effects of 17,18-EEQ-EA and 19,20-EDP-EA on LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells and signaling properties. (A and B) In dose-response studies, BV-2 microglial cells were pretreated with 17,18-EEQ-EA (A) or 19,20-EDP-EA (B) for 4 h followed by LPS (25 ng/mL) stimulation. The culture medium was collected after 24 h and was analyzed for the proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and NO and the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10. LDH production was measured to assess cell toxicity in LPS in stimulated BV-2 microglia (n = 6). (C and D) The potential targets of 17,18-EEQ-EA (C) and 19,20-EDP-EA (D) were studied using AM630 (a CB2-specific inhibitor) and GW9662 (a PPARγ-specific inhibitor) to gauge the reversal of the anti-inflammatory effects by monitoring nitrite production (n = 6). (E–G) Dose–response curves were generated by monitoring the relative luminescence of cannabinoid receptor 1 (CNR1) and cannabinoid receptor 2 (CNR2) PRESTO-Tango gene-transfected HTLA cells as described in SI Appendix, SI Materials and Methods for 17,18-EEQ-EA, EPEA, and CP 55940 (E), 19,20-EDP-EA, DHEA, and CP 55940 (F), and AEA, 2-AG, and CP 55940 (G). Values shown are the mean ± SEM of experiments performed multiple times (n = 3–7). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.