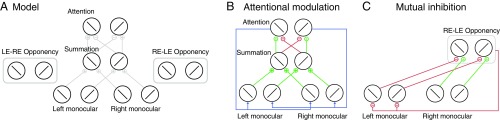
Fig. 1.
Model structure. (A) General structure of the model. For illustration, only some connections between neurons are depicted. The details of the attentional modulation and mutual inhibition are depicted in B and C. (B) Attentional modulation. There are two attention neurons selective for orthogonal orientations. Each attention neuron receives excitatory inputs from the binocular summation neuron that is selective for the same orientation, and suppressive inputs for different orientation. Monocular neurons selective for the same orientation receive the same attention gain factor (blue lines) determined by the response of the attention neuron with the same orientation preference. (C) Mutual inhibition. There are two groups of opponency neurons (RE–LE and LE–RE). Here, only the RE–LE opponency neurons are illustrated. Opponency neurons compute the response difference between the two eyes for a particular orientation. The left-eye (right-eye) monocular neurons are inhibited by the RE–LE (LE–RE) opponency neurons.