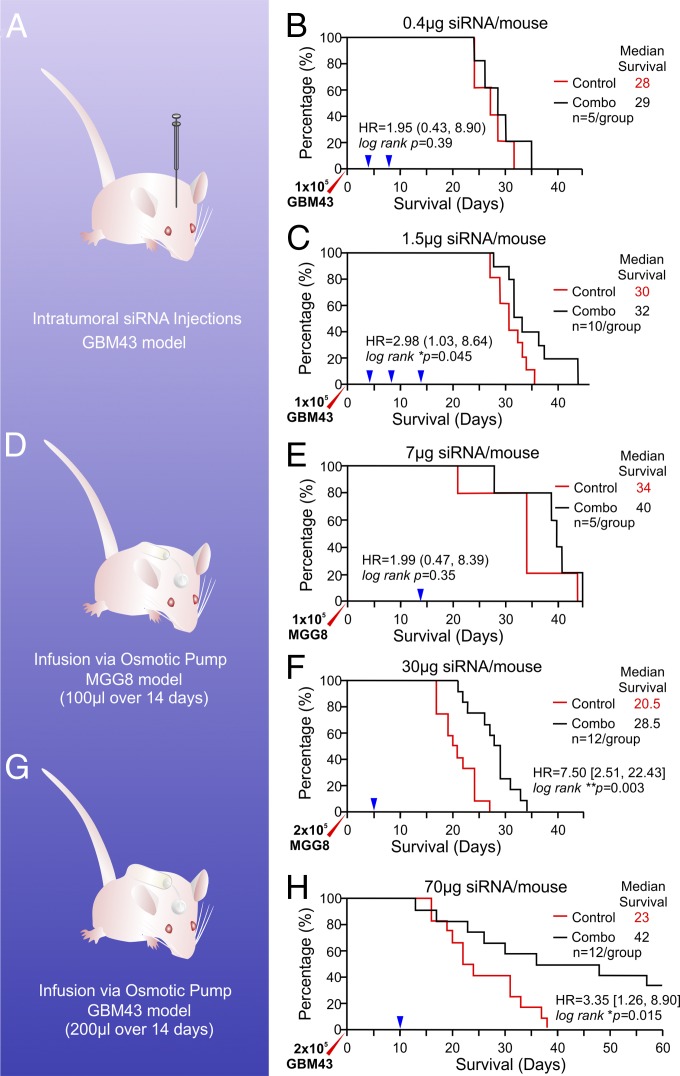
Fig. 7.
In vivo assessment of the survival benefit of nano RNAi on BTIC-driven tumorigenesis. (A) Schematic of the intratumoral bolus injection regimen. (B) Low-dose intratumoral injection (two injections) 4 d after tumor xenograft did not generate survival benefits (n = 5, P = 0.39, log-rank test). (C) A higher drug dose (75 µg/kg) and more redosing (three injections) promoted survival significant benefits for mice with the GBM43 xenograft (*P < 0.05, log-rank test, n = 10), although the medium survival is only 2 d longer than in controls. (D) Schematic of s.c. osmotic pump implantation. (E) A low (7-μg) nano RNAi dose delivered via an s.c.-implanted Alzet pump did not offer significantly longer survival, given the smaller sample size (n = 5), even though there is a median benefit of 6 d. (F) A higher dose (1.5 mg/kg) and larger sample size demonstrated a significant survival benefit for mice with twice as many tumor cell xenografts (n = 12, ***P = 0.003, log-rank test). (G) Schematic of a larger pump implantation. (H) Improved survival profile for xenograft model of GBM43 BTICs (median survival extension = 19 d; log-rank test, *P = 0.015).