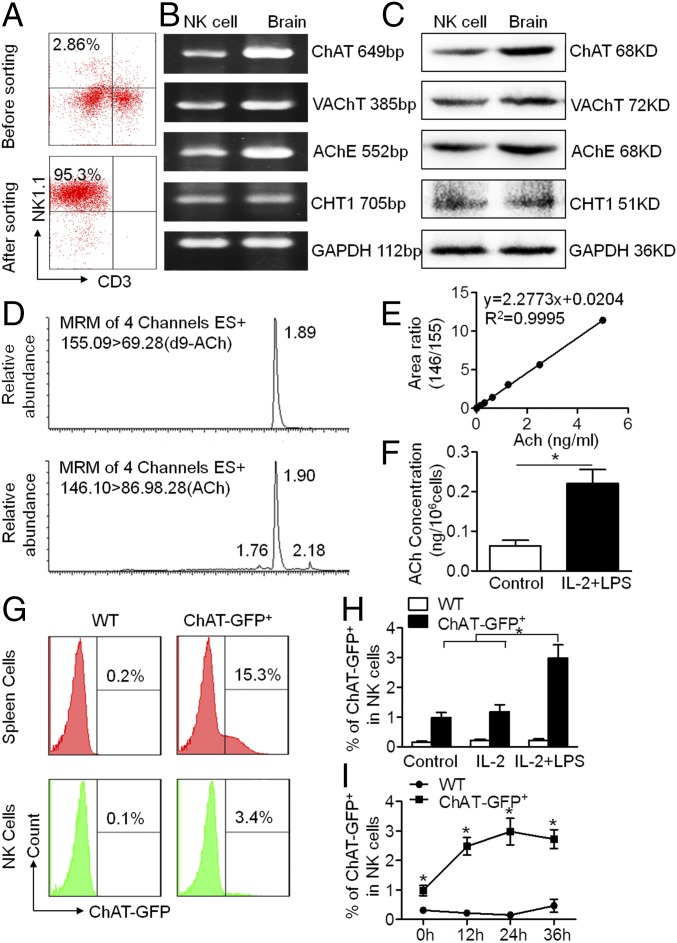
Fig. 1.
Cholinergic system exists in murine NK cells, and acetylcholine synthesis increases under inflammatory stimulation. (A) NK cells (NK1.1+CD3−) from the spleens of C56BL/6 mice were sorted by FACS, producing a purity of above 95%. (B and C) Total mRNA and protein of sorted NK cells were extracted to identify key components of the cholinergic system by RT-PCR and Western blot, compared with the positive control from brain samples. Choline acetyltransferase, vesicular acetylcholine transporter, acetylcholinesterase, and choline transporter 1 were constitutively expressed and synthesized by murine NK cells. n = 5. (D–F) The concentration of intracellular ACh was determined by UPLC-MS/MS with d9-ACh as the internal standard. Intracellular ACh production by NK cells increased under LPS stimulation with IL-2. n = 6 per group from two independent experiments. MRM, multiple reaction monitoring. (G–I) ChAT-eGFP expression in immune cells was counted by FACS. Percentages of ChAT+ spleen immune cells gated by forward and side scatter or spleen NK cells (NK1.1+CD3−) were detected after culture. LPS enhanced ChAT+ expression in NK cells above that in NK cells cultured with IL-2 alone or vehicle control. The percentage of ChAT+ NK cells increased when cultured with IL-2 and LPS and peaked at 24 h following treatment. n = 4 to 6 per group from three independent experiments. Mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.