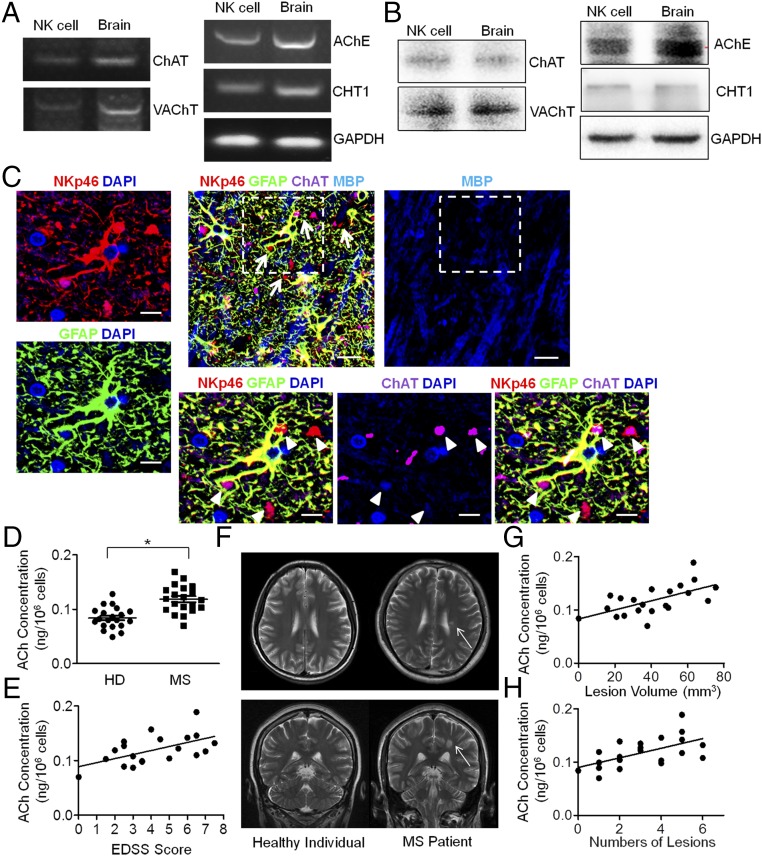
Fig. 8.
Cholinergic system of human NK cells and the up-regulation of ACh synthesis in MS patients. (A and B) Components of the cholinergic system (ChAT, VAChT, AChE, CHT1) were identified in human NK cells by RT-PCR and Western blot, compared with the positive control from brain samples. PCR bands: ChAT, 403 bp; VAChT, 284 bp; AChE, 163 bp; CHT1, 385 bp; GAPDH, 120 bp; Western blot bands: ChAT, 68 kDa; VAChT, 72 kDa; AChE, 68 kDa; CHT1, 51 kDa; GAPDH, 36 kDa. n = 5. (C) Cells with NKp46 expression (Upper Middle) were found mostly in areas with demyelination of white matter, as reflected by the MBP staining (Upper Right). White matter lesions infiltrating NK cells were identified as NKp46+GFAP−, as the arrows indicate (Upper Middle). (Scale bars, 20 μm.) Images with higher magnification of the dashed box indicated area are shown to depict the NK cells (NKp46+GFAP−) (arrowheads) (Lower Left) with ChAT expression (Lower Right). (Scale bars, 8 μm.) Images are representative of six individuals. (D) UPLC-MS/MS detection of intracellular ACh production from human NK cells showed higher levels in MS patients compared with healthy individuals (HD). n = 20 per group. (E) The intracellular ACh concentrations from NK cells of MS patients also correlated with the EDSS scores. n = 20 per group. P < 0.05. (F) Images of axial and coronal T2 MRIs showed hyperintensity of the demyelinated lesions around the peripheral ventricles. Representative images from n = 20 per group. (G and H) MRI scanning showed a positive correlation between intracellular ACh concentration and lesion volume (P < 0.05) or numbers of lesions (P < 0.05). n = 20 per group. Mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05.