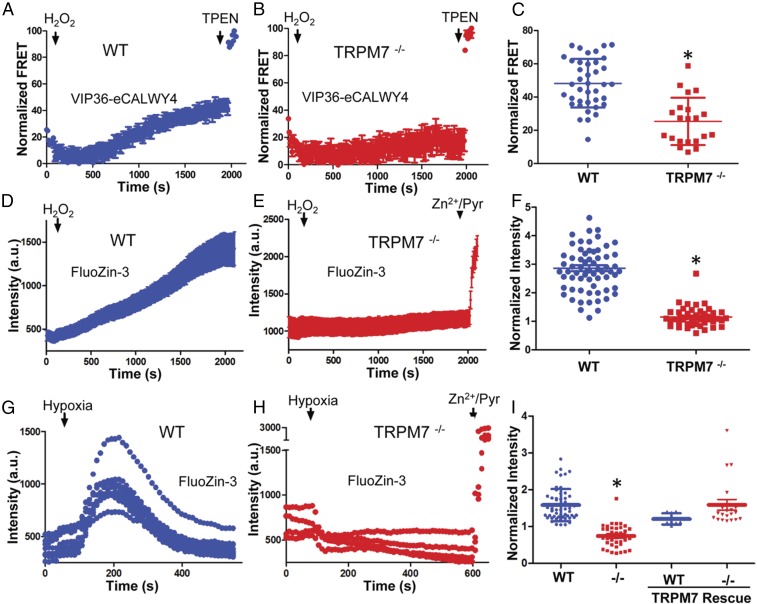
Fig. 7.
TRPM7 is required for ROS-induced Zn2+ release from intracellular stores. (A–C) Zn2+ release from M7Vs was monitored in WT (A and C) or TRPM7−/− (B and C) HEK293T cells expressing the VIP36-eCALWY4 intravesicular Zn2+ sensor. Cells first were incubated with 500 µM Zn2+ and then were perfused with 100 µM H2O2 in Zn2+-free HBT-A containing 250 µM EGTA and 4 mM MgCl2. WT and TRPM7−/− cells were compared by Student’s t test; *P < 0.0001, n = 21–39 cells. (D–F) FluoZin-3–loaded WT (D and F) or TRPM7−/− (E and F) HEK293T cells were similarly loaded with Zn2+ and then were treated with H2O2 in Zn2+-free extracellular medium. The means and SEMs of 44–67 cells are plotted; *P < 0.0001 compared with WT, Student’s t test. (G–I) Experiments were performed as in A–F, but 10 mM sodium dithionite, instead of H2O2, was applied to induce Zn2+ release from intracellular stores, and glucose was omitted from HBT-A. WT mCherry-TRPM7 was overexpressed to rescue the Zn2+ release in TRPM7−/− cells. The means and SEMs of 8–30 cells are plotted; *P < 0.0001 compared with WT, Student’s t test. a.u., arbitrary units.