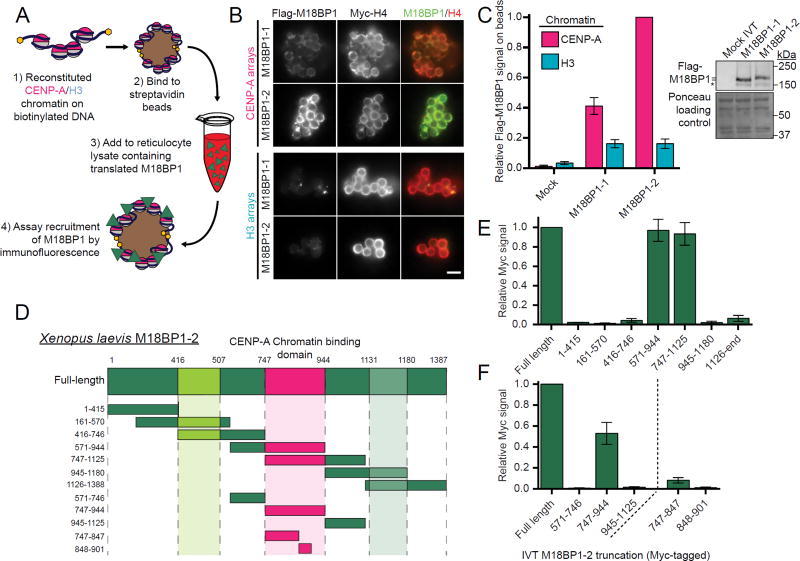
Figure 1. Xenopus M18BP1 directly binds CENP-A chromatin.
A) Schematic of in vitro chromatin binding assay. Reconstituted CENP-A or H3 chromatin, immobilized on streptavidin-coated beads, was incubated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate containing M18BP1. Following chromatin isolation M18BP1 binding was assayed by immunofluorescence.
B) Both isoforms of Xenopus M18BP1 bind selectively to CENP-A chromatin. Representative immunofluorescence images of M18BP1 binding to CENP-A chromatin (top) and H3 chromatin (bottom), both labeled with Myc-tagged histone H4. The M18BP1 isoform is indicated to the left; immunolocalized protein is indicated above. Scale bar, 5 µm.
C) (Left) Quantification of B. Values are normalized to M18BP1-2 signal on CENP-A beads. (Right) Representative Western blot of samples from B. Top portion (anti-Flag) shows similar translation of M18BP1 isoforms; bottom portion (Ponceau stained) is a loading control.
D) Schematic representation of truncations of M18BP1- 2 used to define the CENP-A chromatin binding domain (magenta) in E-F.
E-F) M18BP1-2 binds CENP-A nucleosomes via amino acids 747-944. M18BP1-2 truncations spanning the indicated amino acids were assayed for CENP-A chromatin binding by the method described in A. Values are normalized to full-length M18BP1-2 signal.
All graphs show the mean ± SEM of at least three experiments.
See also Figure S1-S3