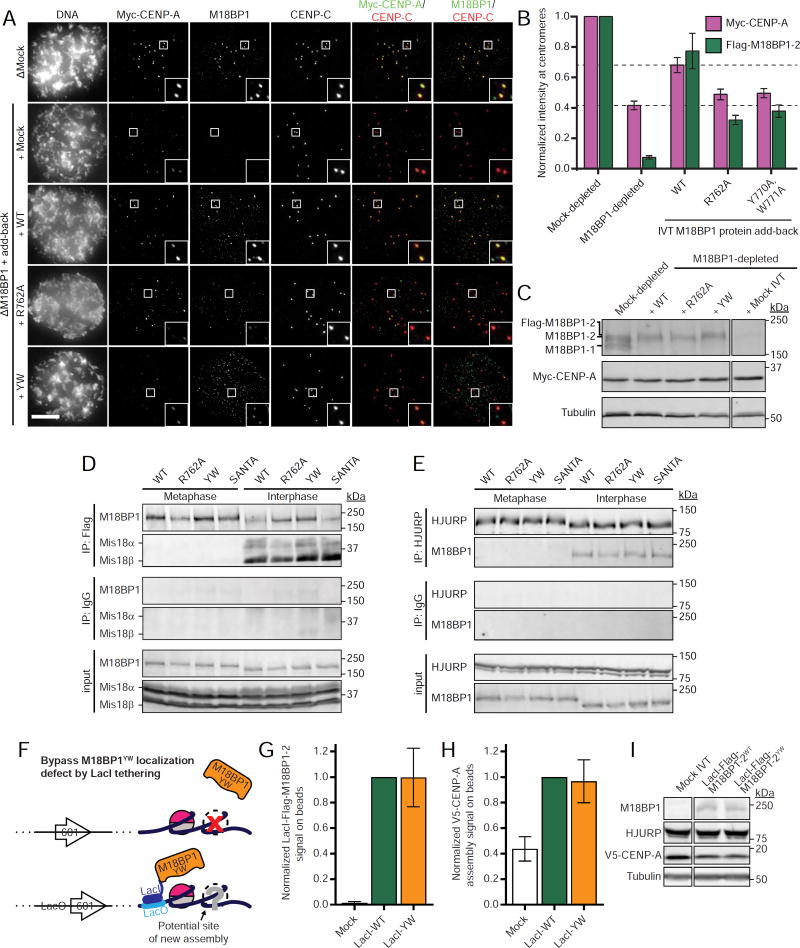
Figure 3. M18BP1 binding to CENP-A nucleosomes is required for CENP-A assembly.
A) M18BP1-2 that cannot bind to CENP-A nucleosomes do not rescue new CENP-A assembly at sperm centromeres. Representative images of sperm nuclei incubated in M18BP1-depleted interphase Xenopus egg extracts complemented with the M18BP1-2 protein indicated at left. Extracts are supplemented with RNA encoding Myc-CENP-A to track new CENP-A assembly and in vitro translated HJURP. The immunolocalized protein is indicated above. Scale bar, 10 µm. Insets magnified 3X.
B) Quantification of A. Values are normalized to the centromere signals in mock-depleted extract. Dashed lines indicate the Myc-CENP-A assembly signal observed upon M18BP1 depletion (bottom) and Flag-M18BP1-2WT add-back (top) as points of reference for mutant rescue.
C) Representative Western blot of CENP-A assembly reactions in A probed with anti-M18BP1 (top), anti-Myc (middle), and anti-tubulin as a loading control (bottom). Efficient M18BP1 depletion is indicated by comparing lanes 1 and 5. Add-back of wild-type or mutant M18BP1-2 is near endogenous levels.
D) Interphase Mis18 complex formation is unaffected by M18BP1 nucleosome binding mutations. Extract depleted of endogenous M18BP1 was supplemented with Myc-Mis18α, Myc-Mis18β, and Flag-M18BP1-2. M18BP1-2 species added to each reaction and cell cycle state of the extract is indicated at the top. Co-immunoprecipitation of Myc-Mis18α/β was assessed by anti-Myc immunoblot following Flag precipitation. Mock precipitations using whole mouse IgG serve as a negative control.
E) HJURP association with M18BP1 is unaffected by CENP-C motif mutations. Extract depleted of endogenous M18BP1 was supplemented with Flag-M18BP1-2. M18BP1-2 species added to each reaction and cell cycle state of the extract are indicated at the top. Coimmunoprecipitation of Flag-M18BP1-2 was assessed by anti-Flag immunoblot following HJURP precipitation. Mock precipitations using whole rabbit IgG serve as a negative control.
F) Schematic of LacI/LacO tethering experiment in G-I. To force localization of mutant M18BP1 to chromatin despite defective nucleosome binding, M18BP1 was fused to the DNA-binding protein LacI. The cognate LacO DNA sequence was inserted into the repeat unit of the nucleosome array DNA such that there is one LacO sequence per 601 nucleosome positioning sequence.
G) Fusion of LacI to Flag-M18BP1-2YW rescues localization to CENP-A chromatin. Quantification of Flag signal on LacO chromatin-coated beads tethered with the indicated LacI-Flag-M18BP1 species.
H) Rescue of M18BP1-2YW localization by artificial tethering rescues CENP-A assembly. Quantification of V5-CENP-A on beads from (G).
All graphs show the mean ± SEM of five experiments.
I) Representative Western blot of samples from G-H. Immunolocalized protein is indicated at the top. M18BP1 immunoblot indicates equivalent levels of LacI-Flag-M18BP1-2 proteins in V5-CENP-A assembly reactions.
See also Figure S4.