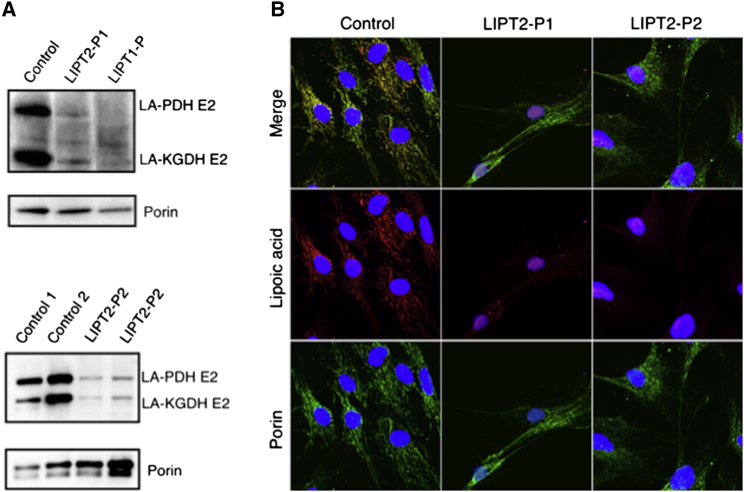
Figure 3.
Immunoblot and Immunofluorescence Staining of Protein-Bound Lipoic Acid
(A) Deficient lipoylation of PDHc and KGDHc E2 subunits in individuals with LIPT2 and LIPT1 mutations. Protein lipoylation was studied by western blot in triplicate with an anti-lipoic acid (Abcam cat# ab58724, RRID: AB_880635, 1:1,600) and anti-porin antibody (Abcam cat# ab14734, RRID: AB_443084, 1:1,000). In fibroblasts from individuals with LIPT2 mutations, the levels of the expected lipoyl-E2 subunits of PDHc and α-KGDHc were strongly decreased, whereas they were undetectable in an individual with LIPT1 deficiency.
(B) Deficient protein lipoylation in fibroblasts of affected individuals. Immunofluorescence staining analysis by a confocal Leica TCS SP8 (Leica) under a 40× NA 1.3 oil immersion objective and acquired using LAS X software revealed decreased protein lipoylation in LIPT2-P1 and LIPT2-P2 fibroblasts (rabbit anti-lipoic acid: Abcam cat# ab58724, RRID: AB_880635, 1:1,000; mouse anti-porin: Abcam cat# ab14734, RRID: AB_443084, 1:400).