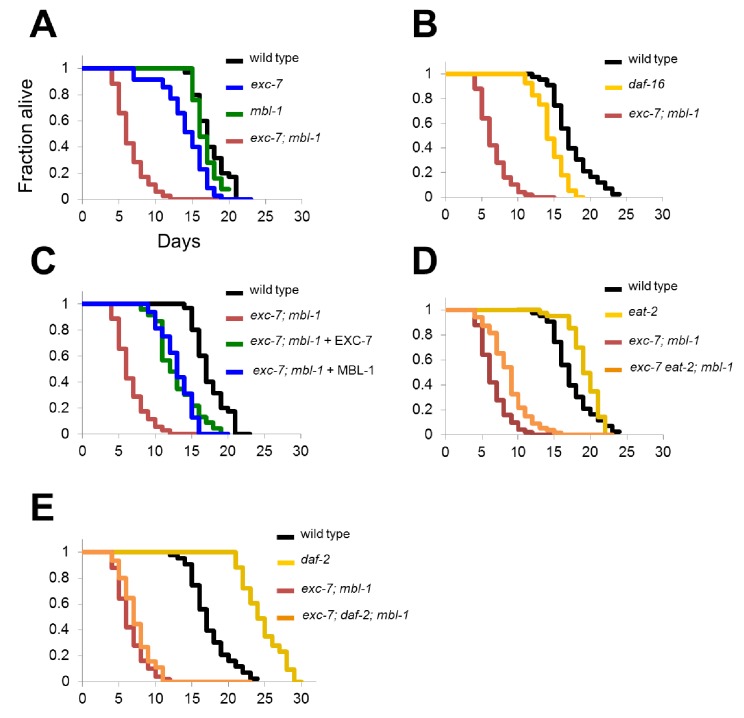
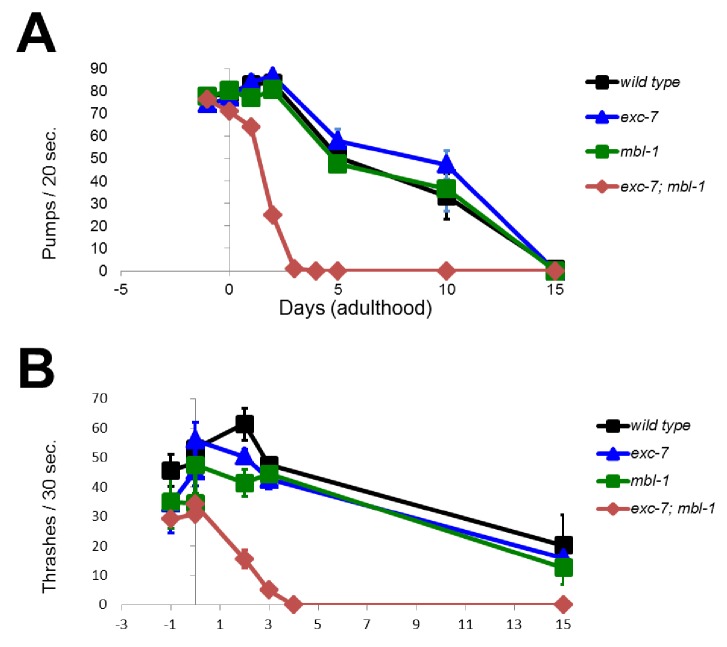
Figure 6. exc-7; mbl-1 mutants have severely shortened lifespans, and genetically interact with the insulin signaling pathway.
(A) exc-7; mbl-1 double mutants, but not single exc-7 or mbl-1 mutants, have strongly reduced lifespans. (B) Lifespan deficits in exc-7; mbl-1 are stronger than the classic short-lived mutant daf-16(mu86). (C) Shortened lifespan in exc-7; mbl-1 mutants can be rescued by transgeneic overexpression of either EXC-7 or MBL-1. (D) eat-2(ad453) mutation increases lifespan in wild-type worms and in exc-7; mbl-1 mutants (p<0.001, log-rank test). (E) daf-2(e1370) mutation strongly increases lifespan in wild-type worms (p<0.001) but not in exc-7; mbl-1 mutants (p>0.05).